This initial charge is referred to as the accumulator
preload.
As an example of accumulator operation, let us
assume that the cylindrical accumulator in figure
12-34 is designed for a preload of 1,300 psi in a 3,000
psi system. When the initial charge of 1,300 psi is
introduced into the unit, hydraulic system pressure is
zero. As air pressure is applied through the air pressure
port, it moves the piston toward the opposite end until it
bottoms. If the air behind the piston has a pressure of
1,300 psi, the hydraulic system pump will have to
create a pressure within the system greater than 1,300
psi before the hydraulic fluid can actuate the piston.
Thus, at 1,301 psi the piston will start to move within
the cylinder, compressing the air as it moves. At 2,000
psi it will have backed up several inches. At 3,000 psi
the piston will have backed up to its normal operating
position, compressing the air until it occupies a space
less than one-half the length of the cylinder.
When actuation of hydraulic units lowers the
system pressure, the compressed air will expand
against the piston, forcing fluid from the accumulator.
This supplies an instantaneous supply of fluid to the
hydraulic system.
Many aircraft have several accumulators in the
hydraulic system. There may be a main system
accumulator and an emergency system accumulator.
There may also be auxiliary accumulators located in
various unit systems. Regardless of the number and
Figure 12-34.--Pressure accumulator, spherical and
their location within the system, all accumulators
cylindrical types.
perform the same function--that of storing an extra
volume of hydraulic fluid under pressure.
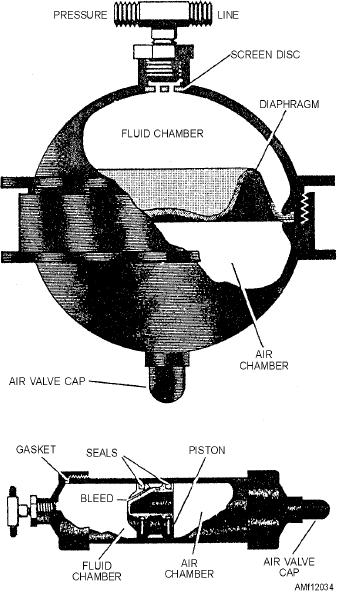
Cylindrical Type
Maintenance
Cylindrical accumulators consist of a cylinder and
Accumulators should be visually examined for
piston assembly. End caps are attached to both ends of
indications of external hydraulic fluid leaks. They
the cylinder. The internal piston separates the fluid and
should then be examined for external air leaks by
air/nitrogen chambers. Both the end caps and piston
brushing the exterior with soapy water, which will
are sealed with gaskets and packings to prevent
form bubbles where the air leaks occur.
external leakage around the end caps and internal
leakage between the chambers. In one end cap, a
The air valve assembly should be loosened to
hydraulic fitting is used to attach the fluid chamber to
examine the accumulator for internal leaks. If
the hydraulic system. In the other end cap, an air filler
hydraulic fluid comes out of the air valve, the
valve is installed to perform the same function as the
accumulator should be removed and replaced. The
filler valve installed in the spherical accumulator.
overhaul or repair of the accumulator is not a line
maintenance function, but it is the responsibility of an
Operation
intermediate-level activity.
The air preload pressure should be checked after
In operation, the compressed-air chamber is
relieving the hydraulic system pressure by operating
charged to a predetermined pressure, which is
the wing flaps or other hydraulically actuated unit. The
somewhat lower than the system operating pressure.
12-35

