TYPES OF STRESS
Q2-5. What is the primary purpose of a stabilizer?
Q2-6. What type of flight controls provides control
Numerous forces and structural stresses act on an
over pitch, roll, and yaw?
aircraft when it is flying and when it is static. When it is
static, gravity force alone produces weight. The weight
Q2-7. What flight control is operated by a
is supported by the landing gear. The landing gear also
side-to-side movement of the control stick?
absorbs the forces imposed during takeoffs and
Q2-8. What type of flight control system is used on
landings.
aircraft that travel at or near supersonic
During flight, any maneuver that causes
speeds?
acceleration or deceleration increases the forces and
Q2-9. What flight control provides lateral control?
stresses on the wings and fuselage. These loads are
Q2-10.
What flight control provides longitudinal con-
tension, compression, shear, bending, and torsion
trol?
stresses. These stresses are absorbed by each
component of the wing structure and transmitted to the
Q2-11.
When is the mechanical control of an F-14
fuselage structure. The empennage, or tail section,
wing sweep used?
absorbs the same stresses and also transmits them to the
Q2-12.
Trim tabs, wing flaps, and speed brakes are
fuselage structure. The study of such loads is called a
all considered what type of flight controls?
"stress analysis." The stresses must be analyzed and
considered when an aircraft is designed. These stresses
Q2-13.
What is the main purpose of a speed brake?
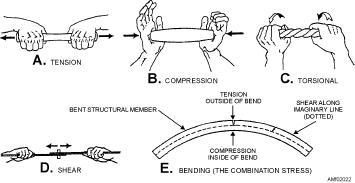
are shown in figure 2-22.
Q2-14.
What type of shock strut is used on all naval
aircraft?
Tension
Q2-15.
What component of a nose landing gear
Tension may be defined as "pull." It is the stress of
resists sudden twisting loads that are applied
stretching an object or pulling at its ends. An elevator
to the nosewheel during ground operation?
control cable is in additional tension when the pilot
Q2-16.
What force is used to raise the arresting hook
moves the control column. Tension is the resistance to
of an aircraft?
pulling apart or stretching, produced by two forces
pulling in opposite directions along the same straight
Q2-17.
What component of a catapult system allows
line.
the aircraft to be secured to the carrier deck?
Q2-18.
What is the major advantage of a helicopter
Compression
over a fixed-wing aircraft?
If forces acting on an aircraft move toward each
Q2-19.
Most Navy helicopters have what fuselage
other to squeeze the material, the stress is called
design?
compression. Compression is the opposite of tension.
Tension is a "pull," and compression is a "push."
STRUCTURAL STRESS
Compression is the resistance to crushing, produced by
two forces pushing toward each other in the same
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Identify the
five basic stresses acting on an aircraft.
Primary factors in aircraft structures are strength,
weight, and reliability. These three factors determine
the requirements to be met by any material used in
airframe construction and repair. Airframes must be
strong and light in weight. An aircraft built so heavy
that it could not support more then a few hundred
pounds of additional weight would be useless. In
addition to having a good strength-to-weight ratio, all
materials must be thoroughly reliable. This reliability
minimizes the possibility of dangerous and unexpected
failures.
Figure 2-22.--Five stresses acting on an aircraft.
2-18

