rubber, self-sealing cells, or bladder-type cells that fit
Q4-46.
What can you use to maintain aerodynamic
into cavities in the wing or fuselage of the aircraft.
smoothness when repairing negligible
damage, steps, and gaps?
Fuel tanks must have facilities for the inspection
and repair of the tank. This requirement is met by
Q4-47.
What step must you take before applying a lap
installing access panels in the fuselage and wings. Fuel
patch over a crack?
tanks must be equipped with sump and drains to collect
Q4-48.
As a general rule, when you make a flush
sediment and water. The construction of the tank must
patch, what is the maximum clearance
be such that any hazardous quantity of water in the tank
between the skin and the filler?
will drain to the sump, so the water can be drained from
Q4-49.
When making a repair over an internal
the fuel tank.
structure, what rivet pattern must you use?
Self-Sealing Fuel Cells
Q4-50.
The main spanwise members designed
primarily to take bending loads on the wing
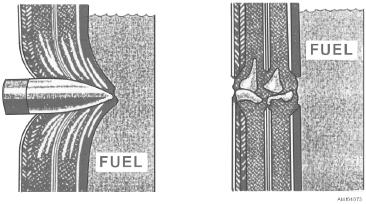
A self-sealing cell is a fuel container that
or other airfoils are known as what type of
automatically seals small holes or damage caused
members?
during combat operations. A self-sealing cell is not
bulletproof, merely puncture sealing. As shown in
Q4-51.
What structural members are designed to give
figure 4-73, the bullet penetrates the outside wall of the
the airfoil shape and rigidity?
cell, and the sticky, elastic sealing material surrounds
Q4-52.
What structural member runs fore-and-aft
the bullet. As the bullet passes through the cell wall into
along the length of the fuselage and is
the cell, the sealant springs together quickly and closes
continuous across frames and bulkheads?
the hole. Now some of the fuel in the tank comes in
contact with the sealant and makes it swell, completing
AIRFRAME FUEL SYSTEM
the seal. In this application, the natural stickiness of
rubber and the basic qualities of rubber and petroleum
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Recognize the
seal the hole. This sealing action reduces the fire hazard
different types of aircraft fuel cells. Identify
brought about by leaking fuel. It keeps the aircraft's fuel
repair procedures for integral fuel cells.
intact so the aircraft may continue operating and return
Airframe fuel system maintenance is the
to its base.
responsibility of more than one work center. For
The most commonly used types of self-sealing fuel
instance, ADs remove and install bladder and
cells are the standard construction type and the type that
self-sealing fuel cells. Personnel of the AM rating
uses a bladder along with the self-sealing cell. Of the
perform the repairs on integral tanks. Personnel from
two, the standard construction cell is used the most. It is
the AO rating usually help in the installation and
a semiflexible cell, made up of numerous plies of
removal of external tanks (drop tanks).
material.
To meet the particular needs of the various types of
aircraft, fuel tanks vary in size, shape, construction, and
location. Sometimes a fuel tank is an integral part of a
wing. Most often fuel tanks are separate units,
configured to the aircraft design and mission.
FUEL TANK CONSTRUCTION
The material selected for the construction of a
particular fuel tank depends upon the type of aircraft
and its mission. Fuel tanks and the fuel system in
general are made of materials that will not react
chemically with any fuels. Fuel tanks that are an
integral part of the wing are of the same material as the
wing. The tank's seams are sealed with fuelproof
Figure 4-73.--Bullet-sealing action.
sealing compound. Other fuel tanks may be synthetic
4-46

