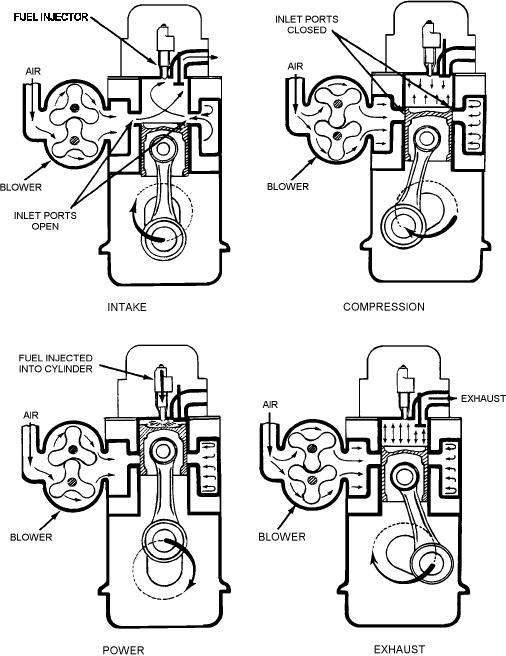
ASf03006
Figure 3-6.--Two-stroke cycle in a diesel engine.
operating at the same speed with conditions being the
It might appear, then, that the 2-stroke cycle could
same.
produce twice as much power as the 4-stroke cycle of
the same size, operating at the same speed. However,
Multiple-Cylinder Engines
this power increase is limited to approximately 70 to 80
percent because some of the power is employed to drive
A single cylinder provides only one power impulse
a blower that forces the air charge into the cylinder
every two crankshaft revolutions in a 4-stroke cycle
under pressure. Also, the burned gases are not
engine and is delivering power only one-fourth of the
completely cleared from the cylinder, which dilutes the
time. To provide for a more continuous flow of power,
combustible mixture in the cylinder, reducing
modern engines use four, six, eight or more cylinders.
combustion efficiency. Additionally, because of the
The same series of cycles previously discussed take
much shorter period the intake port is open (as
place in each cylinder.
compared to the period the intake valve in a 4-stroke is
open), a relatively smaller amount of air is admitted.
In a 4-stroke cycle, 6-cylinder engine, for example,
Hence, with less air, less power per power stroke is
the throws on the crankshaft are set 120 degrees apart,
produced in a 2-stroke cycle engine of like size
the throws for cylinders 1 and 6, 2 and 5, and 3 and 4
3-6

