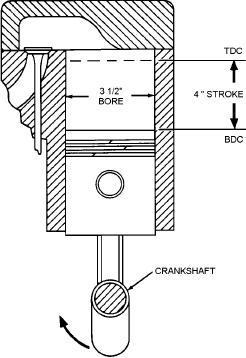
diameter of the cylinder. Stroke is the distance between
INERTIA. Another term you will often encounter
top dead center and bottom dead center. The bore is
is inertia. Inertia is a characteristic of all material
always measured first. For example, a 3.5 4 cylinder
objects. It causes them to resist any change of speed or
means that the cylinder bore, or diameter, is 3.5 inches
direction of travel. A motionless object tends to remain
and the length of the stroke is 4 inches. These
at rest and a moving object tends to keep moving at the
measurements are used to figure piston displacement.
same speed and in the same direction. A good example
of inertia is the tendency of your automobile to keep
Piston displacement is the volume of space that the
moving after your foot is removed from the accelerator.
piston displaces as it moves from one end of the stroke
You apply the brake to overcome the inertia of the
to the other. Thus, the piston displacement in a 3.5-inch
automobile, or its tendency to keep moving.
by 4-inch cylinder would be the area of a 3.5-inch circle
multiplied by 4, the length of the stroke. The area of a
EFFICIENCY. The term efficiency means the
circle is R2 where R is the radius (that is, one-half the
relationship between the actual and theoretical power
diameter) of the circle. Letting S be the length of the
output.
stroke, the formula for the volume (V) is
VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY. Volumetric
V = R2 S
efficiency is the ratio between the amount of fuel-air
mixture that actually enters the cylinder and the amount
If this formula is applied to figure 3-12, the piston
that could enter under ideal conditions. The greater the
displacement is computed as follows:
volumetric efficiency, the greater the amount of fuel-air
R = 1/2 the diameter = 1/2 3.5 in. = 1.75 in.
mixture entering the cylinder; and the greater the
amount of fuel-air mixture, the more power produced
= 3.14
from the engine cylinder.
S = 4 in.
Volumetric efficiency can be improved by using a
then
blower or air-compressing device. On gasoline engines,
this device is called a supercharger. It raises the air
V = 3.14(1.75 in.)2 4 in.
pressure above atmospheric pressure so that the air is
V = 3.14 3.06 in. 4 in.
pushed into the cylinder.
V = 38.43 cubic inches
MECHANICAL EFFICIENCY. Mechanical
efficiency is the relationship between brake horsepower
The total displacement of an engine is found by
(bhp) and indicated horsepower (ihp). Brake
multiplying the volume of one cylinder by the total
horsepower is the actual power put out by the engine,
number of cylinders.
while ihp is the power developed inside the cylinder.
From mechanical efficiency you can tell what
percentage of the power developed in the cylinder is
actually being delivered by the engine. The remaining
percent of power that is not delivered is consumed by
friction, sometimes computed as friction horsepower
(fhp).
THERMAL. The term thermal means, "of or
pertaining to heat." The thermal efficiency of an engine
is the relationship between the power output and the
energy in the fuel burned to produce this output.
Thermal efficiency has a direct relationship to heat
losses in the engine. Because there is a great deal of
heat lost during engine operation, thermal efficiency
usually remains quite low at about 20 to 25 percent.
LINEAR MEASUREMENTS
The size of an engine cylinder is usually indicated
ASf03012
in terms of bore and stroke (fig. 3-12). Bore is the inside
Figure 3-12.--Bore and stroke of an engine cylinder.
3-11

