TOP DEAD CENTER
TDC
INJECTION ENDS
PO
WE
INJECTION
R
BEGINS
ST
28
45
RO
TA
KE
DEG
DEG
TI
O
ST
17 1/2o
o
5
AU ES
H S
EX LO
C
279 DEG
EXHA
E
UST
AK
303 DEG
INT SES
OPEN
S
O
o
CL
48 o 48
PISTON
COVERS
44
VALVE
1/2o
PORTS
CLOSES
71
G
96
o
DE
o
3 1/2
DE
INT
8
G
A
7
KE
ST
AU
PISTON
PISTON
o XH
132 E
COVERS
COVERS
PORTS
PORTS
BDC
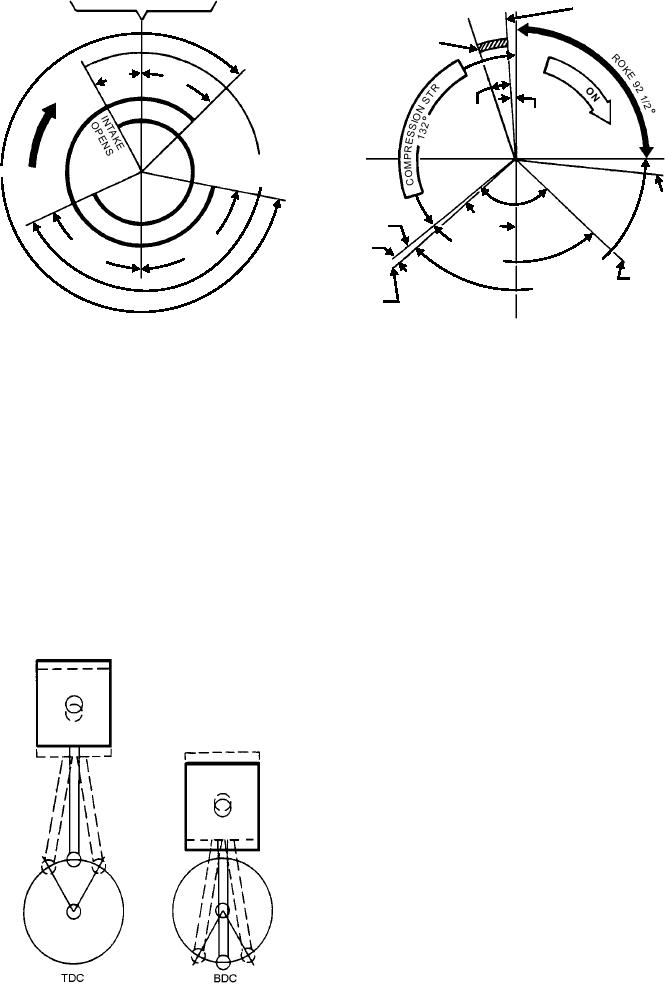
2-STROKE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM
4-STROKE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM
ASf03014
Figure 3-14.--Typical valve timing diagrams.
At higher speeds, there is still less time for the
Ignition Timing
fuel-air mixture to ignite and burn. To compensate for
Ignition timing refers to the timing of the spark
this, and thereby avoid power loss, the ignition system
plug firing with relation to the piston position during
includes both a vacuum and a mechanical advance
the compression stroke. The ignition system is timed so
mechanism that alters ignition timing as engine speed
that the spark occurs before the piston reaches TDC on
increases.
the compression stroke. This gives the mixture enough
Q3-7. What is the major difference in the ignition
time to ignite and start burning. If this time were not
processes of a gasoline and diesel engine?
provided (that is, if the spark occurred at or after TDC),
1. A gasoline engine uses spark plugs to
then the pressure increases would take place too late to
ignite the fuel and a diesel engine heats
provide a full power stroke.
the air in the cylinder by compressing it to
ignite the fuel
2. A gasoline engine uses spark plugs and a
diesel engine uses an igniter coil to ignite
the fuel
3. A gasoline engine uses electronic ignition
and a diesel engine uses an igniter coil to
ignite the fuel
4. A gasoline engine works on the theory of
high compression with low ignition and
the diesel engine works on the theory of
high compression with high ignition
Q3-8. The rate at which work is done is identified by
which of the following terms?
1.
Energy
2.
Power
3.
Inertia
ASf03015
4.
Wattage
Figure 3-15.--Rock positions.
3-13

