Q3-1. What happens to the temperature of a gas
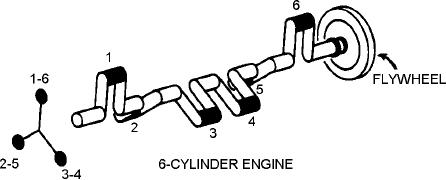
being in line with each other (fig. 3-7). The cylinders
when it is compressed?
fire or deliver the power strokes in the following order:
1-5-3-6-2-4. Thus, the power strokes follow each other
1.
It increases
so closely that there is a fairly continuous and even
2.
It decreases
delivery of power to the crankshaft.
3.
It remains the same
4.
It depends on the original pressure before
Even so, additional leveling off of the power
it is compressed
impulses is desirable, so that the engine will run more
smoothly. The flywheel shown in figure 3-7 is used to
Q3-2. Which of the following items is NOT required
achieve this result.
for an internal combustion engine to operate?
To understand how a flywheel functions, let us
1.
Air
consider a single-cylinder, 4-stroke cycle engine. It is
2.
Humidity
delivering power only one-fourth of the time during the
3.
Fuel
power stroke. During the other three strokes, it is
4.
Ignition
absorbing power to push out the exhaust gas, to pull in a
Q3-3. When a piston is at the top of the stroke, it is in
fresh charge, and to compress the charge. The flywheel
what position?
makes the engine run without varying much in speed
during each revolution. It is a heavy steel wheel
1.
Fully flush
attached to the end of the crankshaft. When it is
2.
Top right angle
rotating, considerable effort is required to slow it down
3.
Fully amass
or stop it. Although the wheel does slow down
4.
Top dead center
somewhat as it delivers power to the engine during the
Q3-4. The intake valves open when the piston is in
exhaust, intake, and compression strokes, the wheel
which of the following positions?
speed increases during the engine power stroke. In
effect, the flywheel absorbs some of the engine power
1.
Traveling in the upward direction
during the power stroke, and then gives it back to the
2.
Nearing the top of the cylinder
engine during the other three engine strokes.
3.
Traveling in the downward direction
4.
At the top of the stroke
In the multicylinder engine, the flywheel functions
in a similar manner, absorbing power when the engine
Q3-5. What is the primary purpose of the flywheel
tends to speed up during the power strokes and giving
on an internal combustion engine?
up power to the engine when the engine slows down
1. It provides a place to attach the trans-
during intervals when little power is being delivered by
mission
the engine.
2. It allows for the attachment of the ring
In addition to the engine itself, which is the power
gear
producer, there must be accessory systems to provide
3. It increases engine torque
the engine with other requirements necessary to operate
4. It allows the engine to run without varying
it. These systems are the fuel system, the lubrication or
in engine speed
oiling system, the electric system, the cooling system,
and an exhaust system.
ASf03007
Figure 3-7.--Crankshaft for a 6-cylinder engine.
3-7

