combustion area of the cylinder. The other opening or
downward with the piston in a straight line. The lower
port permits the burned gases to escape from the
end of the connecting rod moves down and in a circular
cylinder. The two ports have valves in them. These
motion at the same time. This moves the throw and, in
valves, activated by the camshaft, close off either one or
turn, the throw rotates the crankshaft; this rotation is the
the other of the ports, or both of them, during various
desired result. So remember, the crankshaft and
stages of engine operation. The camshaft has a number
connecting rod combination is a mechanism for the
of lobes along its length that open the valves and hold
purpose of changing straight line, or reciprocating
them open for the correct length of time during the
motion, to circular or rotary motion.
piston stroke. The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft
BASIC ENGINE STROKES
through timing gears, or by means of a timing chain. On
a 4-stroke cycle engine, the camshaft turns at one-half
Each movement of the piston from top to bottom or
the crankshaft speed. This permits each valve to open
from bottom to top is called a stroke. The piston takes
and close once for every two revolutions of the
two strokes (an upstroke and a down stroke) as the
crankshaft. One of the valves, called the intake valve,
crankshaft makes one complete revolution. When the
opens to admit an intake of air or a mixture of fuel and
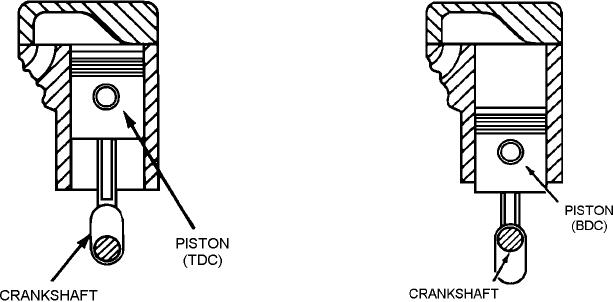
piston is at the top of a stroke (fig. 3-3), it is at top dead
air into the cylinder. The other valve, called the exhaust
center (TDC). When the piston is at the bottom of a
valve, opens to allow the escape of burned gases after
stroke (fig. 3-4), it is at bottom dead center (BDC).
the fuel-and-air mixture has burned.
These positions are called "rock positions" and will be
For the purpose of explanation, we will illustrate
discussed further in this chapter.
the action of a 4-stroke cycle gasoline engine. This type
The basic engine you have studied so far has no
of engine is referred to as a 4-stroke cycle because it
provisions for getting the fuel-air mixture into the
requires four complete strokes of the piston to complete
cylinder or burned gases out of the cylinder. To do this,
one engine cycle. The action of a 4-stroke cycle engine
there are two openings in the enclosed end of a cylinder.
may be divided into four parts: the intake stroke, the
One of the openings, or ports, permits an intake of air or
compression stroke, the power stroke, and the exhaust
an intake of a mixture of fuel and air into the
stroke.
ASf03004
ASf03003
Figure 3-3.--Piston top dead center (TDC).
Figure 3-4.--Piston bottom dead center (BDC).
3-3

