in parallel branches are independent of each other).
means that a small magnetic field is set up by the field
Since field current, and therefore field strength, is not
poles, only a small voltage is induced in the armature.
affected by load current, the output voltage remains
If the resistance of the load decreases, the load current
more nearly constant than does the output voltage of
increases. Under this condition, more current flows
the series-wound generator.
through the field. This increases the magnetic field and
increases the output voltage. In a series-wound dc
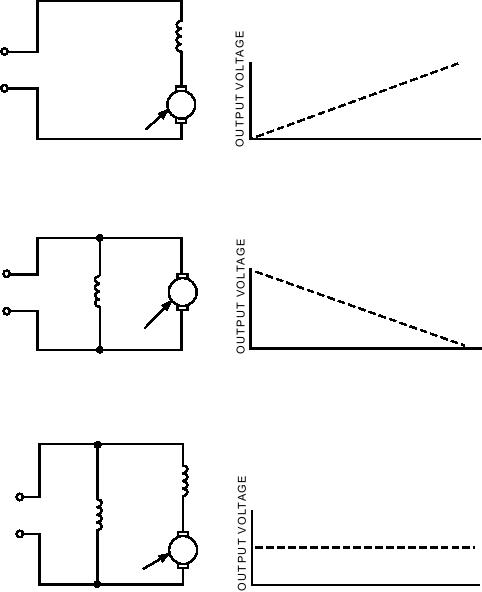
I n a c t u a l u s e , t h e o u t p u t vo l t a g e i n a d c
generator, the output voltage varies with load current.
shunt-wound generator varies inversely as load current
This is undesirable in most applications. For this
varies. The output voltage decreases as load current
reason, this type of generator is rarely used in everyday
increases because the voltage drop across the armature
practice.
resistance increases (E = IR).
S H U N T- W O U N D G E N E R AT O R S . -- I n a
As you have seen, the effect of load current
shunt-wound generator, like the one shown in view B
variation of field strength does not cause voltage
of figure 7-26, the field coils consist of many turns of
variation in the shunt-wound generator. However,
small wire. They are connected in parallel with the
voltage across the armature varies inversely with the
load. In other words, they are connected across the
current.
output voltage of the armature.
In a series-wound generator, output voltage varies
Current in the field windings of a shunt-wound
directly with load current. In the shunt-wound
generator, output voltage varies inversely with load
generator is independent of the load current (currents
SERIES
FIELD
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
LOAD CURRENT
ARMATURE
A . SERIES-WOUND DC GENERATOR
SHUNT
GENERATOR
FIELD
OUTPUT
ARMATURE
LOAD CURRENT
B.
SHUNT-WOUND DC GENERATOR
SERIES
FIELD
SHUNT
GENERATOR
FIELD
OUTPUT
LOAD CURRENT
ARMATURE
C . COMPOUND-WOUND DC GENERATOR
ASf07026
Figure 7-26.--Voltage output characteristics of the series, shunt, and compound-wound generators.
7-17

