should remember that all systems can be broken down
2
into a simplified system (as shown in figures 8-43
5
7
through 8-46). Thus, even the most complex system
1
can be analyzed, not from the standpoint of a complex
system but from that of a simple system.
TYPES OF HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS
ss
There are two types of hydraulic systems used in
6
4
3
support equipment, open-center and closed-center.
Open-Center System
RETURN
PRESSURE
SUCTION
An open-center system is one that has fluid flow
ASf08045
Actuating cylinder
5. Relief valve
1.
but no pressure in the system whenever the actuating
Reservoir
6. Check valve
2.
mechanisms are idle. Fluid circulates from the
Power pump
7. Pressure regulator
3.
reservoir, through the pump, through the directional
Selector valve
4.
valves, and back to the reservoir. Pressure developed in
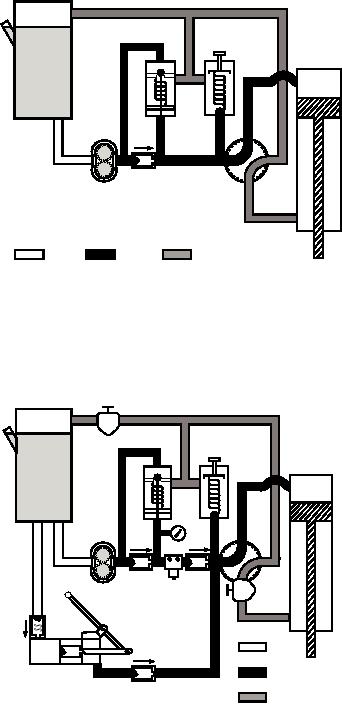
Figure 8-45.--Hydraulic system with a relief valve and
regulator incorporated.
an open-center system is controlled by open-center
Directional valves and is limited by a system relief
valve. Figure 8-47 shows an open-center system. Note
2
14
the position of the directional valves and the fact that
5
the valves are connected in series. In this type of
7
1
system, there is no pressure in the system until one of
the subsystems is actuated by the positioning of the
8
directional valve. When in the neutral position (view
13
3
A), the open-center directional valve directs the fluid
ss
ss
to the return line. When the directional valve is
4
positioned out of neutral, pressure builds up in the
9
6
10
actuating section and operates the selected mechanism
(view B). When an open-center system is not being
12
SUCTION
used (no actuating mechanisms), the pump is said to be
ss
11
idling because there is no pressure buildup in the
PRESSURE
ss
system. Therefore, there is no load on the pump. Fixed
RETURN
ASf08046
displacement pumps are used in open-center systems
Actuating cylinder
8. Reservoir standpipe
1.
and normally do not require a pressure regulator.
Reservoir
9. Check valve
2.
Power pump
10. Pressure line filter
3.
Closed-Center System
Selector valve
11. Check valve
4.
Relief valve
12. Hand pump
5.
Check valve
13. Pressure gauge
6.
A closed-center system always has fluid stored
Pressure regulator
14. Return line filter
7.
under pressure whenever the pump is operating.
Figure 8-46.--Complete hydraulic system.
However, when pressure is built up to a predetermined
value, the load is automatically removed from the
mentioned, this system includes more check valves, a
pump by a pressure regulator or the integral control
pressure gauge, filters, and a hand pump. The hand
valve of the variable displacement pump. The
pump is added as an auxiliary system, normally used as
h y d r a u l i c s y s t e m s h ow n i n fi g u r e 8 - 4 6 i s a
an emergency power source in case of failure of the
closed-center system. In a closed-center system,
main power pump.
multiple Directional valves are arranged in parallel
The complete hydraulic system may be further
rather than in series, as in an open-center system.
expanded by including a pressure manifold, more
N OT E : S o m e s y s t e m s m a y e m p l o y b o t h
selector valves, actuating mechanisms, and more
power-driven pumps connected in parallel. But, you
open-center and closed-center features.
8-37

