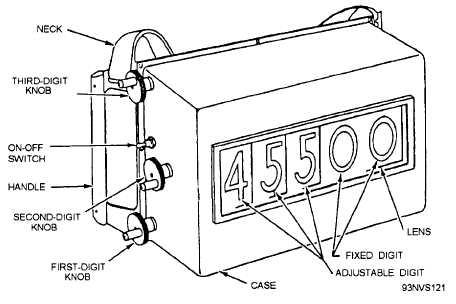
Figure 4-59.—Weight confirmation unit.
recommended that the unit be operated during the day
without batteries installed to reduce the weight of the
unit and extend battery life. For night operations, four
size D batteries are installed. The ON/OFF switch
controls an electroluminescent lamp at the front or the
back of the unit. The back of the unit is equipped with
a panel, on which the operator can write with a grease
pencil. The unit is held by the operator at waist level on
an adjustable neck strap. The operator sets the particular
aircraft weight to appear on the front of the unit, and
then flashes the weight to the pilot in the aircraft and to
the catapult officer.
CATAPULT CONTROL SYSTEMS
The control system of a steam catapult controls all
phases of catapult operation. The operation of the
control system is primarily divided between the main
control console and the deckedge control panel on the
C-7/C-11 and C-13 catapults. On the C-13-1 and
C-13-2 catapults, the controls are centrally located in
the ICCS.
Electrical Control System Components
The electrical control system for a steam catapult
consists of a control console and various control panels
that govern the operation of the catapult in conjunction
with control components of other systems.
Included among the components of the catapult
electrical control system are various push buttons,
switches, solenoids, relays, circuit breakers, fuses, and
lights. The control console is the focal point of all
functions of the catapult electrical control systems.
Electrically operated solenoid valves produce
mechanical operation of valves throughout the catapult.
Some solenoid valves are actuated by buttons, while
others function automatically during catapult operation.
Various changes that occur during catapult operation are
sensed by limit switches and pressure switches.
Operation of these switches actuates lights at various
control panels. The following paragraphs briefly
describe some of these components. For information on
the function and interrelationship of the electrical
components in a specific system, study the schematic
diagrams in the technical manual for that particular type
of catapult.
SOLENOIDS.—A solenoid is an electromagnet
formed by a conductor wound in a series of loops in the
shape of a helix (spiral). Inserted within this spiral or
coil are a soft-iron core and a movable plunger. The
soft-iron core is pinned or held in position and therefore
is not movable. This movable plunger (also soft iron) is
held away from the core by a spring in the de-energized
position. See figure 4-60.
When current flows through the conductor, a
magnetic field is produced. This field acts in every
respect like a permanent magnet having both a north
and south pole.
As shown in figure 4-60, the de-energized position
of the plunger is partially out of the coil, because of the
action of the spring. When voltage is applied, the
4-47