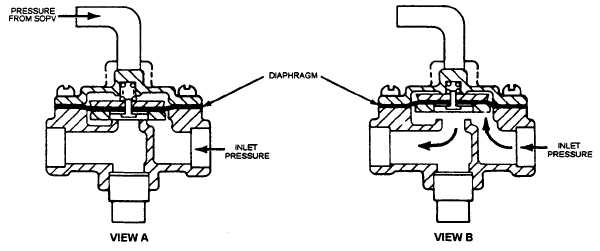
Hytrol Valve
The hytrol valve (fig. 5-5) either isolates inlet
pressure from the pressure-reducing control valve, or
vents inlet pressure to the pressure-reducing control
valve and the fuel port of the main valve. Pressure
directed from the SOPV to the top of the diaphragm
holds the hytrol valve closed. When this pressure is
vented (also through the SOPV), the inlet pressure
opens the hytrol valve allowing fuel flow. No adjust-
ments are made to the hytrol valve. It is either open
or closed.
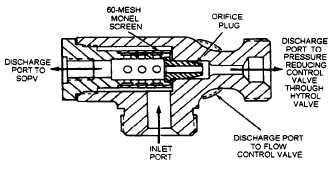
Ejector-Strainer
The ejector-strainer (fig. 5-6) reduces inlet pres-
sure to the pressure-reducing control valve, and
filters fuel. It consists of an orifice plug and a 60-
mesh monel screen located between the inlet port and
three discharge ports. The orifice plug creates
reduced pressure by increasing fuel velocity (like an
eductor). This aids in vacating the cover chamber of
the fuel valve. The monel screen traps foreign
particles and contaminating substances. The three
discharge ports direct filtered fuel to the pressure-
reducing control valve, the flow control valve, and the
SOPV.
Solenoid-Operated Pilot Valve (SOPV)
The SOPV (fig. 5-7) shifts the Cla-Val assembly
from the defuel to the fuel mode of operation, and vice
versa. The SOPV is a direct acting, solenoid-actuated
valve. It is a four-way valve with a grooved stem that
moves back and forth in a machined bore inside the
body. When the solenoid is energized in the fueling
mode, the stem is drawn against spring compression
by the magnetic pull of the solenoid. When the
solenoid is deenergized in the defueling mode, the
Figure 5-6.—Ejector strainer.
the stem is returned by the extension of the core
spring. Movement of the valve piston directs full flow
in one direction or full flow in the opposite direction.
There is no closed-port position. The valve is also
equipped with a manual operator. Manual operation
is done by pushing upward on the button at the lower
end of the control. A quarter-turn clockwise locks the
manual operator in place.
The solenoid is housed in an explosion-proof case
and meets the requirements for use in hazardous
locations.
Flow Control Valve (Needle Valve)
The flow control valve (fig. 5-8) consists of a
needle valve with a spring and disk assembly within
a housing. The housing cover can he removed to allow
for needle valve adjustment. The flow control valve is
installed in the line between the ejector-strainer and
the fuel valve cover chamber.
The flow control valve, by virtue of its construction,
controls the flow from the fuel valve cover chamber,
Figure 5-5.—Hytrol valve.
5-4