A transponder signal reinforces the radar signal
transponder transmission goes to the ground
normally seen on the radarscopes. It makes the
interrogator-receiver, which is processed through a
signal stronger and much less susceptible to
computer. It is then displayed in alphanumeric form
atmospheric interference.
on the controller's radar screen. The length of the
round-trip transit time determines the range of the
The beacon system altitude reporting feature may
replying aircraft. The mean direction of the main
reduce vertical separation in the higher flight levels.
beam of the interrogator antenna during the reply
determines the azimuth. The encoded signal from the
It continuously updates aircraft altitude records
transponder provides, via mode C, the aircraft's
in 100-foot increments. This permits more ac-
altitude in 100-foot increments.
curate traffic control when aircraft are chang-
ing altitude rapidly, as they do in terminal areas.
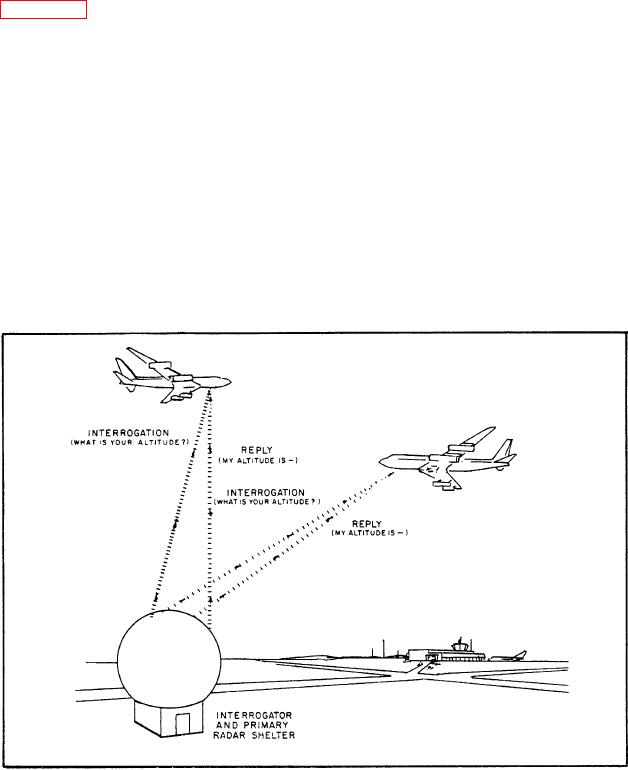
Look at figure 6-20, which shows the automatic
altitude reporting system. As you can see, a
semiautomated air traffic control system includes the
The AIMS Program
following improvements over the past system:
The AIMS Program, implemented by the
It automatically provides the air traffic controller
Department of Defense, derives its name from the
with a radar presentation. It identifies, in three
following acronyms:
dimensions, every properly equipped aircraft within
his/her control area.
ATCRBS (air traffic control radar beacon system)
IFF (identification friend or foe)
As a result of the three-dimensional presentation,
it greatly reduces the use of voice radio. It also eases
MARK XII Identification System
the workload of the air traffic controller, thus
Systems (reflecting the many AIMS configurations)
increasing air traffic control efficiency.
Figure 6-20.--The automatic altitude reporting system.

