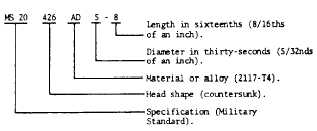
A letter or letters following the head-shaped code
identify the material or alloy from which the rivet was
made. Table 2-1 includes a listing of the most
common of these codes. The alloy code is followed
by two numbers separated by a dash. The first
number is the numerator of a fraction, which specifies
the shank diameter in thirty-seconds of an inch. The
second number is the numerator of a fraction in
sixteenths of an inch, and identifies the length of the
rivet. The rivet code is shown in figure 2-2.
Rivet Composition
Most of the rivets used in aircraft construction are
made of aluminum alloy. A few special-purpose
rivets are made of mild steel, Monel, titanium, and
copper. Those aluminum alloy rivets made of 1100,
2117, 2017,2024, and 5056 are considered standard.
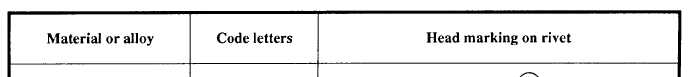
ALLOY 1100 RIVETS.—Alloy 1100 rivets are
supplied as fabricated (F) temper, and are driven in
this condition. No further treatment of the rivet is
required before use, and the rivet’s properties do not
change with prolonged periods of storage. They are
relatively soft and easy to drive. The cold work
resulting from driving increases their strength
slightly. The 1100-F rivets are used only for riveting
nonstructural parts.
These rivets are identified by
their plain head, as shown in table 2-1.
ALLOY 2117 RIVETS.—Like the 1100-F rivets,
these rivets need no further treatment before use and
can be stored indefinitely. They are furnished in the
solution-heat-treated (T4) temper, but change to the
Figure 2-2.—Rivet coding example.
solution-heat-treated and cold-worked (T3) temper
after driving. The 2117-T4 rivet is in general use
throughout aircraft structures, and is by far the most
widely used rivet, especially in repair work. In most
cases the 2117-T4 rivet may be substituted for
2017-T4 and 2024-T4 rivets for repair work by using
a rivet with the next larger diameter. This is desirable
since both the 2017-T4 and 2024-T4 rivets must be
heat treated before they are used or kept in cold
storage. The 2117-T4 rivets are identified by a
dimple in the head.
ALLOY 2017 AND 2024 RIVETS.—As
mentioned in the preceding paragraph, both these
rivets are supplied in the T4 temper and must be heat
treated. These rivets must be driven within 20
minutes after quenching or refrigerated at or below
32°F to delay the aging time 24 hours. If either time
is exceeded, reheat treatment is required. These rivets
may be reheated as many times as desired, provided
the proper solution heat-treatment temperature is not
exceeded. The 2024-T4 rivets are stronger than the
2017-T4 and are, therefore, harder to drive. The
Table 2-1.—Rivet Material Identification
2-2