another fluid is a heat exchanger. Distilling plants,
MRG lube oil coolers, fuel oil transfer heaters,
and fuel oil service heaters are primary examples
of heat exchangers; in common usage, however,
they are not referred to as heat exchangers.
For heat to transfer from one substance to
another, a difference in the temperature of the
two substances must exist. Heat flow or heat
transfer can occur only from a substance that is
at a higher temperature to a substance that is at
a lower temperature. When two objects that are
at different temperatures are placed in contact
with one another, or near each other, heat will
flow from the warmer object to the cooler one
until both objects are at the same temperature.
Heat transfer occurs at a faster rate when there
is a large temperature difference than when there
is only a slight temperature difference. As the
temperature difference approaches zero, the rate
of heat flow also approaches zero.
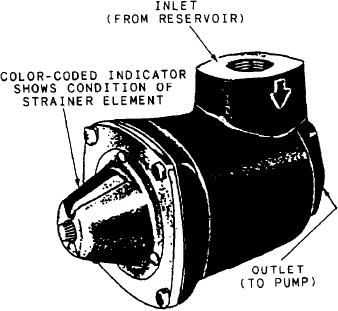
Figure 6-32.--Color-coded indicating filter.
In some heat exchangers we want to RAISE
THE TEMPERATURE of one fluid. Fuel oil
heaters, combustion air preheaters, lube oil
filter/separator sump is removed through a drain
heaters, and many other heat exchangers used
line, either automatically or manually.
aboard ship serve this function.
In other heat exchangers, we want to LOWER
In-Line or Cone Filter
THE TEMPERATURE of one fluid. Lube oil
coolers, start air coolers, and bleed air coolers are
In-line or cone filters have conical-shaped fine
examples of this type of heat exchanger.
mesh screen or perforated metal sheet that is
In this section we describe some of the heat
inserted into the system pipe and secured by a set
exchangers that you will find in the engineering
of flanges. Its system application determines
spaces.
whether it is considered a filter or strainer. It is
most commonly used in seawater systems, where
CLASSIFICATION OF
it is considered a strainer. This type of filter is
HEAT EXCHANGERS
prohibited in fuel systems.
Heat exchangers may be classified according
MAINTENANCE
to the path of heat flow, the relative direction of
the flow of the fluids, the number of times either
Proper operation of filters, strainers, and filter
fluid passes the other fluid, and the general
separators is essential for satisfactory gas turbine
construction features, such as the type of surface
and diesel engine performance. Besides clogging
and the arrangement of component parts. The
the systems with foreign matter, continued
types of heat exchangers in common use in naval
operation with unfiltered fluids results in
ships are described in the following sections by
accelerated pump wear and system degradation.
these basic methods of classification.
Routine maintenance of filters, strainers, and
filter/separators is adequately covered in Naval
Type of Surface
S h i p s ' Technical Manual, Chapter 541,
"Petroleum Fuel Stowage, Use, and Testing,"
Surface heat exchangers are known as PLAIN
paragraphs 541-8.51 through 541-8.59.
SURFACE units if the surface is relatively
smooth, or as EXTENDED SURFACE units if
the surface is fitted with rings, fins, studs, or some
HEAT EXCHANGERS
other kind of extension. The main advantage of
the extended surface unit is that the extensions
Any device or apparatus designed to allow the
increase the heat transfer area without requiring
transfer of heat from one fluid (liquid or gas) to
6-21

