Proportional-Flow Filters
how clean or dirty the element is. Another feature
of this type of filter is the ease and speed with
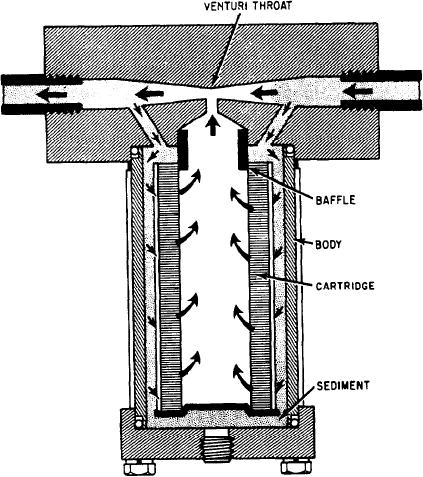
A proportional-flow filter (fig. 6-31) may use
which the element can be removed and replaced.
the Venturi effect to filter a portion of the fluid
Most filters of this kind are designed for inlet line
flow. The fluid can flow in either direction. As
installation.
it passes through the filter body, a venturi throat
causes an increase in velocity and a decrease in
pressure. The pressure difference forces some of
Filter/Separator
the fluid through the element to rejoin the main
stream at the venturi. The amount of fluid filtered
The filter/separator is a two-stage unit
is proportional to the flow velocity. Hence the
consisting of a coalescer stage and a separator
name proportional-flow filter.
stage within a single housing. Each stage is made
up of replaceable elements, the number of which
Indicating Filters
is determined by such considerations as the
capacity of the elements in gallons per minute
Indicating filters are designed to signal the
(gpm) and the elements dirt retaining properties.
operator when the element needs cleaning. There
Coalescer elements filter solids from the fluid and
are various types of indicators, such as color-
cause small particles of undissolved water to
coded, flag, pop-up, and swing arm. Figure 6-32
combine (coalesce) into larger drops of water that,
shows a color-coded indicating filter. The element
because of their weight, will settle in the
is designed so it begins to move as the pressure
filter/separator sump. Separator elements are
increases due to dirt accumulation. One end is
provided to remove any remaining free water that
linked to an indicator that shows the operator just
has not coalesced. Water that accumulates in the
Figure 6-31.--Proportional-flow filter.
6-20

