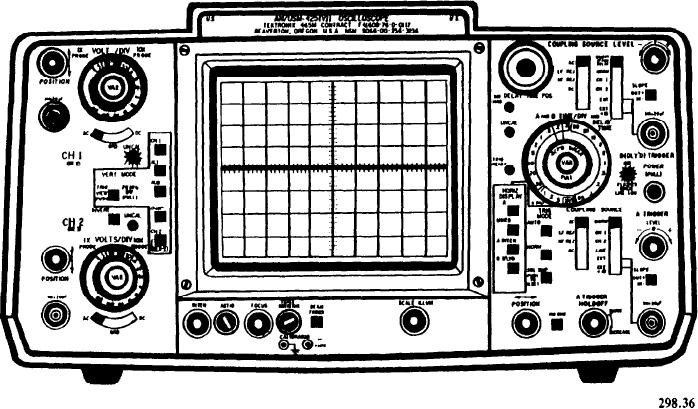
Figure 3-38 shows the front panel of a dual-trace,
SIGNAL GENERATORS
general-purpose oscilloscope. It is commonly used
in the fleet.
The many types of signal generators (oscil-
lators) vary from relatively simple test instruments
to highly accurate laboratory models. Their
Oscilloscopes vary greatly in the number
of controls and connectors. Usually, the more
function is to produce ac of the desired frequency
controls and connectors, the more versatile
and amplitudes.
the instrument. Regardless of the number, all
One of the primary uses of a signal generator
oscilloscopes have similar controls and con-
is to set power turbine (PT) speed trip set points.
nectors. Once you learn the fundamental opera-
Figure 3-39 shows a typical wide-range oscillator.
tion of these common controls, you can move
with relative ease from one model of oscillo-
FREQUENCY COUNTERS
scope to another. Occasionally, controls that
Many different types of frequency counters
serve similar functions will be differently
are available. They vary from relatively simple
labeled from one model to another. However, you
will find that most controls are logically grouped
test instruments to highly accurate instruments.
and that their names usually indicate their
Frequency counters function to measure frequen-
function.
cies that already exist.
You can use a frequency counter in con-
junction with the signal generator to check the
The oscilloscope in figure 3-38 is referred to
output frequency of a signal generator for more
as a DUAL-TRACE OSCILLOSCOPE. It
accepts and displays two vertical signal inputs at
accuracy.
the same time--usually for comparison of the two
HYDROMETER
signals or one signal and a reference signal. This
scope can also accept just one input. In this case
it is used as a SINGLE-TRACE OSCILLO-
You will be responsible for maintaining the
SCOPE.
batteries for the uninterruptible power supply
Figure 3-38.--Dual-trace oscilloscope.
3-28

