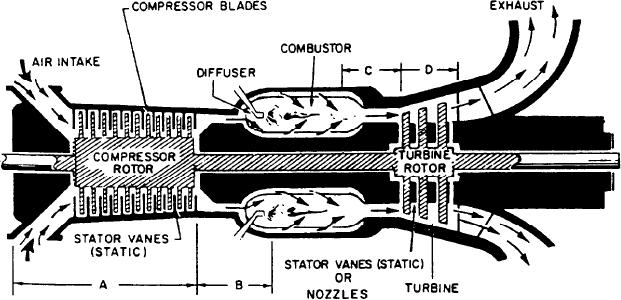
discussed earlier. A review of the gas turbine
Air is drawn into the front of the compressor.
process is detailed as follows:
The rotor is so constructed that the area decreases
toward the rear. This tapered construction gives
1. Air is taken in through the air inlet duct by
a convergent area (area A).
the compressor. There it is raised in pressure and
Between each rotating stage is a stationary
discharged into the combustion chamber (or
stage or stator. The stator partially converts high
combustor).
velocity to pressure and directs the air to the next
2. Fuel is admitted into the combustion
set of rotating blades.
chamber by the fuel nozzle(s). The fuel-air
Because of its high rotational speed and the
mixture is ignited by an igniter(s) (not shown) and
aerodynamic shape of its blades, the rotor
combustion occurs.
increases the velocity of the air. Each pair of rotor
3. The hot and rapidly expanding gases are
and stator blades constitutes a pressure stage.
directed aft through the turbine rotor assembly.
Both a pressure increase and a reduction in
There, thermal and kinetic energy are converted
volume occurs at each stage (Boyle).
into mechanical energy. The gases are then
This process continues at each stage until the
directed out through the exhaust duct.
air charge enters the diffuser (area B). There is
a short area in the diffuser where no further
CONVERGENT-DIVERGENT PROCESS
changes take place. As the air charge approaches
the end of the diffuser, you will notice that the
Several pressure, volume, and velocity changes
opening flares (diverges) outward. At this point,
occur within a GTE during operation. The
the air loses velocity and increases in volume and
convergent-divergent process is an application of
pressure. The velocity energy has become pressure
Bernoulli's principle. (If a fluid flowing through
energy, while pressure through the diffuser has
a tube reaches a constriction or narrowing of the
remained constant. The reverse of Bernoulli's
tube, the velocity of the fluid flowing through the
principle and Boyle's law has taken place. The
constriction increases and the pressure decreases.
compressor continuously forcing more air through
The opposite is true when the fluid leaves the
this section at a constant rate maintains constant
constriction; velocity decreases and pressure
pressure. Once the air is in the combustor,
increases.) Boyle's law and Charles's law
combustion takes place at constant pressure. After
(discussed in NAVEDTRA 10563, volume 1,
combustion there is a large increase in the volume
chapter 4) also come into play during this
of the air and combustion gases (Charles's law).
process. Refer to figure 1-8 as we apply these laws
The combustion gases go rearward to area C.
to the GTE.
This occurs partially by velocity imparted by the
Figure 1-8.--Convergent-divergent process.
1-7

