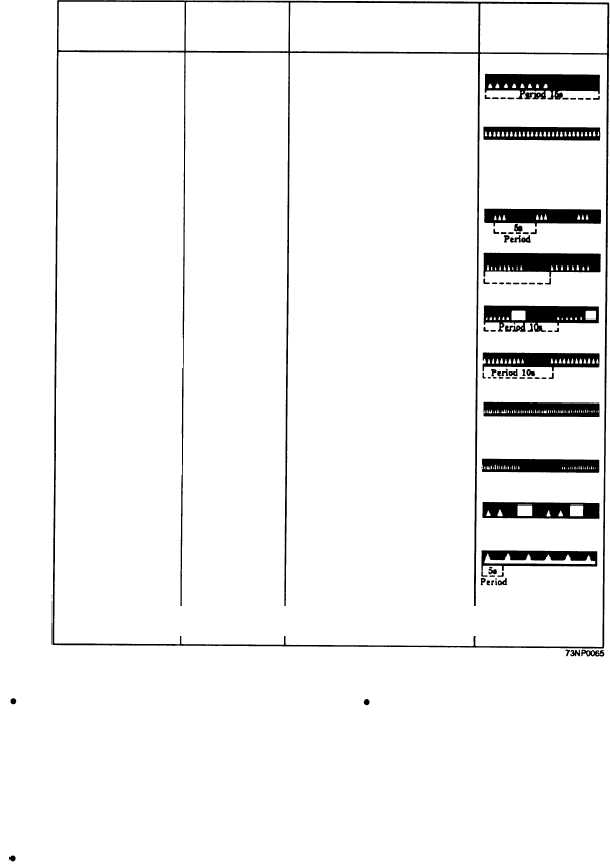
CLASS
ABBREVIATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ILLUSTRATION
Interrupted quick light
IQ, Int Qk Fl
A light in which the sequence of quick
flashes is interrupted by regularly
repeated eclipses of constant and long
duration.
Continuous very quick light
VQ, Qk Fl
A very quick light in which a flash is
regularly repeated. Flashes are repeated
at a rate of not less than 80 flashes per
minute but less than 160 flashes per
minute.
Group very quick light
VQ (3), Gp Fl (3)
A very quick light in which a specified
group of flashes is regularly repeated.
VQ (9), Gp Fl (9)
VQ (6) + LFl, Gp Fl
6 + LFl
Interrupted very quick light
IVQ, Int Qk Fl
A light in which the sequences of quick
flashes is interrupted by regularly
repeated eclipses of constant and long
duration.
Continuous ultra quick light
UQ, Qk, Fl
An ultra quick light in which a flash is
regularly repeated. Flashes are repeated
at a rate of not less than 160 flashes per
minute.
Interrupted ultra quick light
IUQ
An ultra quick light in which the se-
quence of flashes is interrupted by
eclipses of long duration.
Morse code light
Mo (U)
A light in which appearances of light of
two clearly different durations are
grouped to represent a character or
characters in the Morse Code.
Fixed and flashing light
FFl
A light in which a fixed light is com-
bined with a flashing light of higher
luminous intensity.
Alternating light
A1, A1t
A light showing different colors alter-
nately.
Notes: 1. Alternating lights may be used in combined
2. The second abbreviation shown for a light if
form with most of the previous classes of lights.
any, is alternate U.S. useage.
Figure 9-8.—Characteristics of lights—sheet 2.
Luminous range: Maximum distance at which a
light can be seen under the existing visibility conditions.
It depends only on the intensity of the light itself and
is independent of the elevation of the light, the
observer's height of eye, or the curvature of Earth. It
should be noted that luminous range and nominal
range are equal with a meteorological visibility of 10
nautical miles.
Computed range: The geographic range plus the
observer's distance to the horizon based on the
observer's height of eye.
LIGHTHOUSES AND LIGHT
STRUCTURES
Lighthouses are numerous on all the coasts of the
United States, on the Great Lakes, and along many
interior waterways. They are placed wherever a
powerful light may be of assistance to navigators, or
wherever a danger requires a warning beacon of
long-range visibility. Visibility increases with height;
Computed visibility: Determined for a particular
light, taking into account its elevation, intensity, height
of eye of the observer, and the curvature of Earth.
9-9