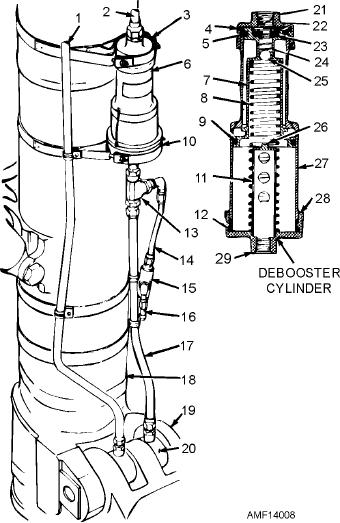
20. Brake shuttle valve
11. Riser tube
1. Emergency system pressure line
21. Inlet port
12. Packing
2. Main brake pressure line
22. Snapring
13. Tee fitting
3. Upper support clamp
23. Spring retainer
14. Brake line (to pressure relief valve)
4. Packing
24. Valve spring
15. Brake pressure-relief valve
5. Packing
25. Ball
16. Overflow line
6. Debooster cylinder assembly
26. Ball pedestal
17. Brake line (debooster to shuttle
7. Piston
27. Barrel
valve)
8. Piston return spring
28. Lower end cap
18. Shock strut
9. Packing
29. Outlet port
19. Torque link
10. Lower support clamp
Figure 14-8.--Brake debooster cylinder.
(due to a loss of fluid from the brake unit or connecting
the piston to the large end of the piston. As the piston
lines), the piston will continue to move downward until
moves downward in the housing, a new flow of fluid is
the riser unseats the ball check valve in the hollow
created from the large end of the housing through the
shaft. With the ball check valve unseated, fluid from
outlet port to the brake. Because the force from the
the power control valve will pass through the piston
small piston head is distributed over the greater area of
shaft to replace the lost fluid. Since the fluid passing
the large piston head, pressure at the outlet port is
through the piston shaft acts on the large piston head,
reduced. At the same time, a greater volume of fluid is
the piston will move up, allowing the ball check valve
displaced by the large piston head than that used to
to seat when pressure in the brake assembly becomes
move the small piston head.
normal.
Normally, the brake will be fully applied before the
When the brake pedal is released, pressure is
piston has reached the lower end of its travel. However,
removed from the inlet port, and the piston return
if the piston fails to meet sufficient resistance to stop it
14-7

