action. When pedal pressure is released, the brakes
to both sides of the center carrier, and to the housing
assembly, which makes a total of 16 pucks.
should release without any evidence of drag. All
disc-type brakes must be checked periodically for
When hydraulic pressure is applied to the pistons,
lining wear. Excessively worn linings must be
the pucks are forced against the first disc, which
replaced.
contacts the pucks in the center carrier. This force
moves the center carrier and its pucks against the
Lining wear may be checked by two methods. The
second disc, forcing it in contact with the pucks in the
method used depends upon the model of the brake
housing. In this manner, each disc receives equal
assembly. Both methods are described later in this
braking action on both sides as the pressure is
chapter. Before checking the brakes on any aircraft,
increased. When brake pressure is released, the return
always refer to the applicable MIM and use the method
springs force the pistons back to the preset clearance
recommended by the aircraft manufacturer.
between the pucks and the disc. The self-adjusting
feature is identical to that described for the single disc
DUAL DISC BRAKES
brakes. Maintenance of the dual disc brake is the same
as that previously given for the single disc type.
Dual disc brakes are used on aircraft where more
braking friction is desired with lower pressures.
MULTIPLE/TRIMETALLIC DISC BRAKES
The dual disc brake is very similar to the single
Multiple disc brakes are heavy-duty brakes
disc type, except that two rotating discs, instead of one,
designed for use with power brake control valves or
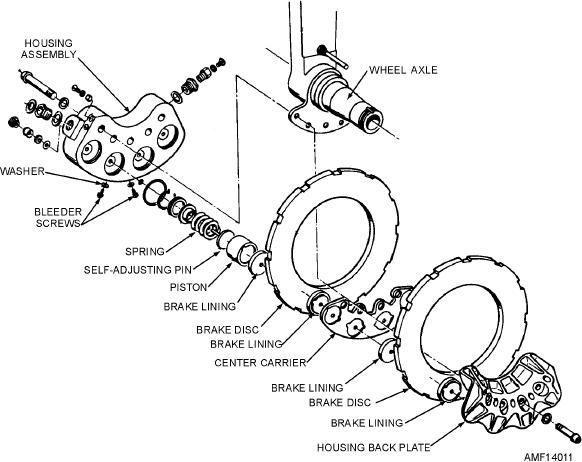
are used. One model of this brake is shown in figure
power boost master cylinders. The brake assembly
14-11.
consists of a bearing carrier; bearings and retaining
The unit consists of a housing assembly, a center
nut; the annular actuating piston; and the heat stack,
carrier assembly, and two rotating discs. The housing
which is composed of a pressure plate, rotating discs
assembly contains four cylinders, each of which
(rotors), stationary discs (stators) and backup plate, an
contains a piston, a return spring, and a self-adjusting
automatic adjuster, retracting springs, and various
other components.
pin. Brake linings (pucks) are attached to each piston,
Figure 14-11.--Dual disc brake.
14-10

