narrow, it may not be strong enough to bear the load
short, the threads of the bolt will extend into the bolt
imposed on it. If the head is too thick or too wide, it may
hole and may act like a reamer when the material is
extend so far that it interferes with the movement of
vibrating. To prevent this, make certain that no more
adjacent parts.
than two threads extend into the bolt hole. Also make
certain that any threads that enter the bolt hole extend
BOLT HEADS.--The most common type of head
only into the thicker member that is being fastened. If
is the hex head. See figure 3-11. This type of head may
the grip is too long, the nut will run out of threads
be thick for greater strength or relatively thin in order to
before it can be tightened. In this event, a bolt with a
fit in places having limited clearances. In addition, the
shorter grip should be used, or if the bolt grip extends
head may be common or drilled to lockwire the bolt. A
only a short distance through the hole, a washer may be
hex-head bolt may have a single hole drilled through it
used.
between two of the sides of the hexagon and still be
A second bolt dimension that must be considered is
classed as common. The drilled head-hex bolt has three
diameter. Figure 3-10 shows that the diameter of the
holes drilled in the head, connecting opposite sides of
bolt is the thickness of its shaft. If this thickness is 1/4
the hex.
of an inch or more, the bolt diameter is usually given in
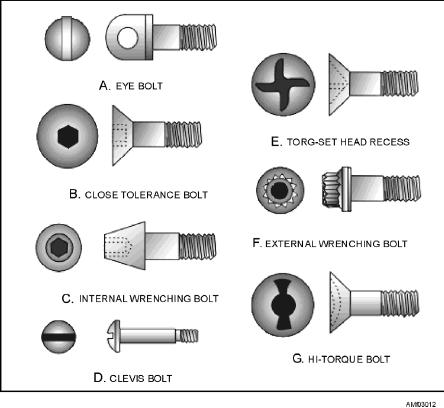
Seven additional types of bolt heads are shown in
fractions of an inch; for example, 1/4, 5/16, 7/16, and
figure 3-12. Notice that view A shows an eyebolt, often
1/2. However, if the bolt is less than 1/4 of an inch thick,
used in flight control systems. View B shows a
the diameter is usually expressed as a whole number.
countersunk-head, close-tolerance bolt. View C shows
For instance, a bolt that is 0.190 inch in diameter is
an internal-wrenching bolt. Both the countersunk-head
called a No. 10 bolt, while a bolt that is 0.164 inch in
bolt and the internal-wrenching bolt have hexagonal
diameter is called a No. 8.
recesses (six-sided holes) in their heads. They are
The results of using a bolt of the wrong diameter
tightened and loosened by use of appropriate sized
should be obvious. If the bolt is too big, it cannot enter
Allen wrenches. View D shows a clevis bolt with its
the bolt hole. If the diameter is too small, the bolt has
characteristic round head. This head may be slotted, as
too much play in the bolt hole, and the chances are that
shown, to receive a common screwdriver or recessed to
it is not as strong as the correct bolt.
receive a Reed-and-Prince or a Phillips screwdriver.
The third and fourth bolt dimensions that should be
View E shows a torque-set wrenching recess that
considered when choosing a bolt replacement are head
has four driving wings, each one offset from the one
thickness and width. If the head is too thin or too
opposite it. There is no taper in the walls of the recess.
Figure 3-12.--Bolt Heads.
3-7

