Washers
MACHINE SCREWS.--The commonly used
machine screws are the flush-head, round-head,
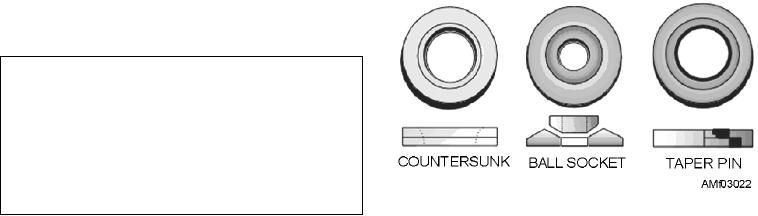
Washers such as ball socket and seat washers, taper
fillister-head, socket-head, pan-head and truss-head
pin washers, and washers for internal-wrenching nuts
types.
and bolts have been designed for special applications.
Flush Head.--Flush-head machine screws are
See figure 3-22.
used in countersunk holes where a flush finish is
Ball socket and seat washers are used where a bolt
desired. These screws are available in 82 and 100
is installed at an angle to the surface, or where perfect
degrees of head angle, and have various types of
alignment with the surface is required at all times.
recesses and slots for driving.
These washers are used together.
Round Head.--Round-head machine screws are
Taper pin washers are used in conjunction with
frequently used in assembling highly stressed aircraft
threaded taper pins. They are installed under the nut to
components.
effect adjustment where a plain washer would distort.
Fillister Head.--Fillister-head machine screws are
Washers for internal-wrenching nuts and bolts are
used as general-purpose screws. They may also be used
used in conjunction with NAS internal-wrenching
as cap screws in light applications, such as the
bolts. The washer used under the head is countersunk to
attachment of cast aluminum gearbox cover plates.
seat the bolt head or shank radius. A plain washer is
Socket Head.--Socket-head machine screws are
used under the nut.
designed to be screwed into tapped holes by internal
wrenching. They are used in applications that require
Turnlock Fasteners
high-strength precision products, compactness of the
assembled parts, or sinking of the head into holes.
Turnlock fasteners are used to secure panels that
require frequent removal. These fasteners are available
Pan and Truss Head.--Pan-head and truss-head
in several different styles and are usually referred to by
screws are general-purpose screws used where head
the manufacturer's trade name.
height is unimportant. These screws are available with
cross-recessed heads only.
CAMLOC FASTENERS.--The 4002 series
Camloc fastener consists of four principal parts: the
SELF-TAPPING SCREWS.--A self-tapping
receptacle, the grommet, the retaining ring, and the stud
screw is one that cuts its own internal threads as it is
assembly. See figure 3-23. The receptacle is an
turned into the hole. Self-tapping screws can be used
aluminum alloy forging mounted in a stamped sheet
only in comparatively soft metals and materials.
metal base. The receptacle assembly is riveted to the
Self-tapping screws may be further divided into two
access door frame, which is attached to the structure of
classes or groups: machine self-tapping screws and
the aircraft. The grommet is a sheet metal ring held in
sheet metal self-tapping screws.
the access panel with the retaining ring. Grommets are
Machine self-tapping screws are usually used for
furnished in two types: the flush type and the
attaching removable parts, such as nameplates, to
protruding type. Besides serving as a grommet for the
castings. The threads of the screw cut mating threads in
hole in the access panel, it also holds the stud assembly.
the casting after the hole has been predrilled. Sheet
The stud assembly consists of a stud, a cross pin, a
metal self-tapping screws are used for such purposes as
temporarily attaching sheet metal in place for riveting.
They may also be used for permanent assembly of
nonstructural parts, where it is necessary to insert
screws in blind applications.
CAUTION
Self-tapping screws should never be used to
replace standard screws, nuts, or rivets in the original
structure. Over a period of time, vibration and stress
will loosen this type of fastener, causing it to lose its
holding ability.
Figure 3-22.--Various types of special washers.
3-12

