Most hydraulic systems are equipped with return
be consulted for adjustment procedures for the pedal
lines between the actuating units and the reservoir. The
linkage. The master cylinder must be serviced and the
fluid circulates from the reservoir, through the supply
system bled before the brakes are ready for service.
lines, through the actuating units, and back to the
However, before this is accomplished, all necessary
reservoir. This allows any air in the system to escape
repairs should be made to the wheel cylinders.
through the reservoir vent during circulations.
Wheel Cylinder Repair.--Wheel cylinders are
Brake hydraulic systems, however, are not
rebuilt in much the same manner as a master cylinder.
equipped with return lines; therefore, there is no means
To do this, it is seldom necessary to remove the
for the air to escape. Air in the system will cause the
cylinder assembly from the brake backing plate.
action of the brake pedal to feel soft and spongy
However, before the cylinder can be repaired, the brake
because air is compressible. The hydraulic brake
assemblies must be removed.
system must be bled to expel this air.
To disassemble a wheel cylinder with two pistons
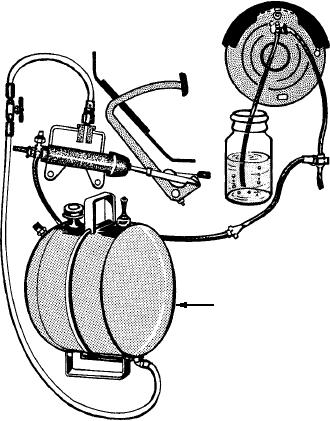
There are two common methods of bleeding a
(fig. 2-39), pull the boots from the cylinder and push
hydraulic brake system--the pressure method and the
the pistons, cups, and spring out of the cylinder.
manual method. The pressure method employs a brake
After the parts are removed, clean the cylinder wall
bleeder tank, which delivers fluid under pressure to the
and check for pits and accumulation of rust. A small
master cylinder (fig. 2-40).
quantity of pits or rust at the exact center of the cylinder
Before pressurizing the bleeder tank for use,
should not affect the operation of the wheel cylinder. If
ensure that the tank has an adequate supply of the
the rust or pits are just inside the outermost polished
required type of brake fluid and that the valve on the
areas of the cylinder bore, they must be removed by
discharge line is closed.
honing. Cylinders containing deep pits or scratches
must be replaced.
Manufacturers usually recommend that the master
cylinder reservoir be filled with hydraulic fluid before
After honing a cylinder, remove all the abrasive
connecting the pressure tank. Make sure there is a tight
dust and lubricate the cylinder walls with clean, new
seal between the adapter cap and the master cylinder
hydraulic fluid. The pistons are usually made of
filler port. Then, apply pressure to the master cylinder
aluminum, and unless badly scored, they may be
by opening the valve on the discharge line of the tank.
reused indefinitely. However, they should not be
sanded--only cleaned with an approved solvent or
clean, hydraulic brake fluid.
After the cylinder bore is satisfactorily cleaned and
lubricated, lubricate the cup seals. Insert a cup into the
end of a cylinder. Do not push the cup through the bore.
As soon as the lips of the cup are in the bore, use the
piston to move the cup into place.
Installing the other cup and piston may be more
difficult, since the cup retaining spring will push
against the cup and piston already installed. With one
hand, hold the one piston from pushing out, and with
the other hand, install the spring, cup, and piston. Then,
install the boots and brake shoe links, rods, or slugs.
Install a wheel cylinder clamp or use a cord or wire to
tie a loop around the cylinder to hold the components in
PRESSURE TANK
the cylinder until the brake shoes are installed.
Bleeding Hydraulic Brake Systems.--During
repair of the master brake cylinder or wheel cylinders,
or anytime a brake line is disconnected, air will enter
the hydraulic brake system. Also, when the fluid level
ASf02040
in the reservoir is allowed to become too low, air will
Figure 2-40.--Bleeding hydraulic system--pressure method.
enter the brake lines.
2-32

