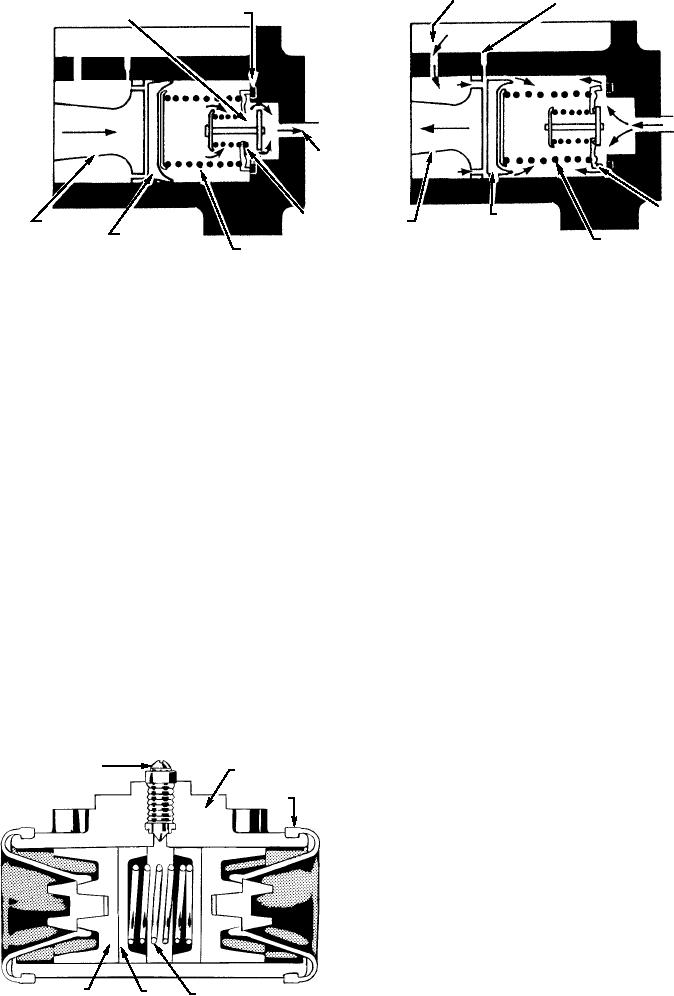
BREATHER
COMPENSATING PORT
CAGE SEAT
PORT
CHECK VALVE
BRAKE
BRAKE
LINE
LINE
VALVE
PRIMARY
CAGE
VALVE
PISTON
PISTON
CUP
SEAT
PRIMARY
RETURN
CUP
RETURN SPRING
SPRING
ASf02038
PRESSURE APPLIED
PRESSURE RELEASED
Figure 2-38.--Hydraulic brake master cylinder--operation of two-way valve.
seal at the wheel cylinder cup packing and prevents air
The two pistons in the cylinder move in opposite
from entering the system.
directions under hydraulic pressure. Through a short
stem, the pistons push the shoes against the drum.
Wheel Cylinder.--The wheel cylinder may be of
These stems are connected directly to the shoes.
almost any design or exterior shape to suit the need, but
all wheel cylinders work on the same basic principle
Rubber cup seals fit tightly in the cylinder bore
and fulfill the requirements of moving the brake shoes
against each piston to prevent the escape of fluid.
into contact with the drum. There are two basic
Between the cups is a light spring to keep the cups in
designs--a single-piston type and a double-piston
position against the pistons. The open ends of the
type, sometimes called uniservo and duoservo
cylinder are fitted with rubber boots to keep out foreign
cylinders, respectively. Different combinations of
matter.
these two types of cylinders are used on different
Brake fluid enters the cylinder from the brake line
models of equipment.
connection between the pistons. A bleeder port and
Figure 2-39 illustrates a double-piston wheel
valve are located at the top of the cylinder between the
cylinder. The single-piston is similar, only smaller
pistons. This provides a means for releasing air from
because it has only one piston. This unit, regardless of
the system.
whether single- or double-piston type, changes the
Various applications of wheel cylinders are used in
applied fluid pressure into mechanical force to move
support equipment, depending upon the
the brake shoes. The wheel cylinder housing, made
m a n u f a c t u r e r 's d e s i g n . S o m e m a y h a v e o n e
from a casting, is bolted to the brake backing plate.
single-piston cylinder or a dual-piston cylinder per
wheel, each operating two shoes. Others may use a
BLEEDER SCREW
CYLINDER
combination of one single and one dual piston or two
HOUSING
dual pistons per wheel. When a dual system is used,
BOOT
each cylinder is mounted diametrically opposite the
other, and each operates one end of two shoes.
I N S P E C T I O N A N D M A I N T E NA N C E . --
Hydraulic brake systems must be inspected at
specified intervals. A visual inspection includes
checking the fluid level in the master cylinder
reservoir, the security of mounting bolts and clamps,
the condition of tubing and hoses, and the entire system
for leaks. When the wheels and drums are removed for
PISTON
ASf02039
CUP
RETURN SPRING
inspection of the brake assemblies, the wheel cylinder
Figure 2-39.--Hydraulic brake wheel cylinder.
should be inspected for leaks. The boots may be pulled
2-30

