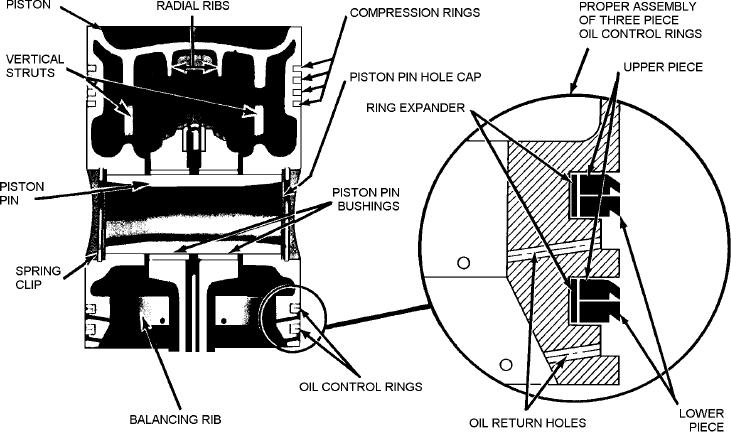
generated during operation, it becomes round because
and rings than the pistons of gasoline engines. Some of
the expansion is proportional to the thickness of the
these rings may be installed below as well as above the
metal. The walls of the skirt are cut away as much as
wrist or piston pin (fig. 3-27).
possible to reduce weight and to prevent excessive
Fitting pistons properly is important. Because
expansion during engine operation. Many aluminum
metal expands when heated, and because space must be
pistons are made with split skirts so that when the
provided for lubricants between the pistons and the
pistons expand the skirt diameter will not increase.
cylinder walls, the pistons are fitted to the engine with a
Two types of piston skirts found in most engines
specified clearance. This clearance depends upon the
are the full trunk and the slipper. The full-trunk type
size or diameter of the piston and the material from
skirt has a full cylindrical shape with bearing surfaces
which it is made. Cast iron does not expand as fast or as
parallel to those of the cylinder, giving more strength
much as aluminum. Aluminum pistons require more
and better control of the oil film. The slipper-type
clearance to prevent binding or seizing when the engine
(cutaway) skirt has considerable relief on the sides of
gets hot. The skirt or bottom part of the piston runs
the skirt, providing clearance for crankshaft
much cooler than the top; therefore, it does not require
counterweights and leaving less area for possible
as much clearance as the head.
contact with the cylinder walls, and thereby reducing
The piston is kept in alignment by the skirt, which
is usually cam ground (elliptical in cross section), as
indicated in figure 3-28. This elliptical shape permits
PISTON PINS.--The piston is attached to the
the piston to fit the cylinder, regardless of whether the
connecting rod by means of the piston pin (wrist pin).
piston is cold or at operating temperature. The
The pin passes through the piston pin bosses and
narrowest diameter of the piston is at the piston pin
through the upper end of the connecting rod, which
bosses, where the metal is thickest. At the widest
rides within the piston on the middle of the pin. Piston
diameter of the piston, the piston skirt is thinnest. The
pins are made of alloy steel with a precision finish and
piston is fitted to close limits at its widest diameter so
are case hardened and sometimes chromium-plated to
that piston noise (slap) is prevented during engine
increase their wearing qualities. Their tubular
warm-up. As the piston is expanded by the heat
construction gives them a maximum of strength with a
ASf03027
Figure 3-27.--Piston assembly of General Motors series 71 diesel engine.
3-24

