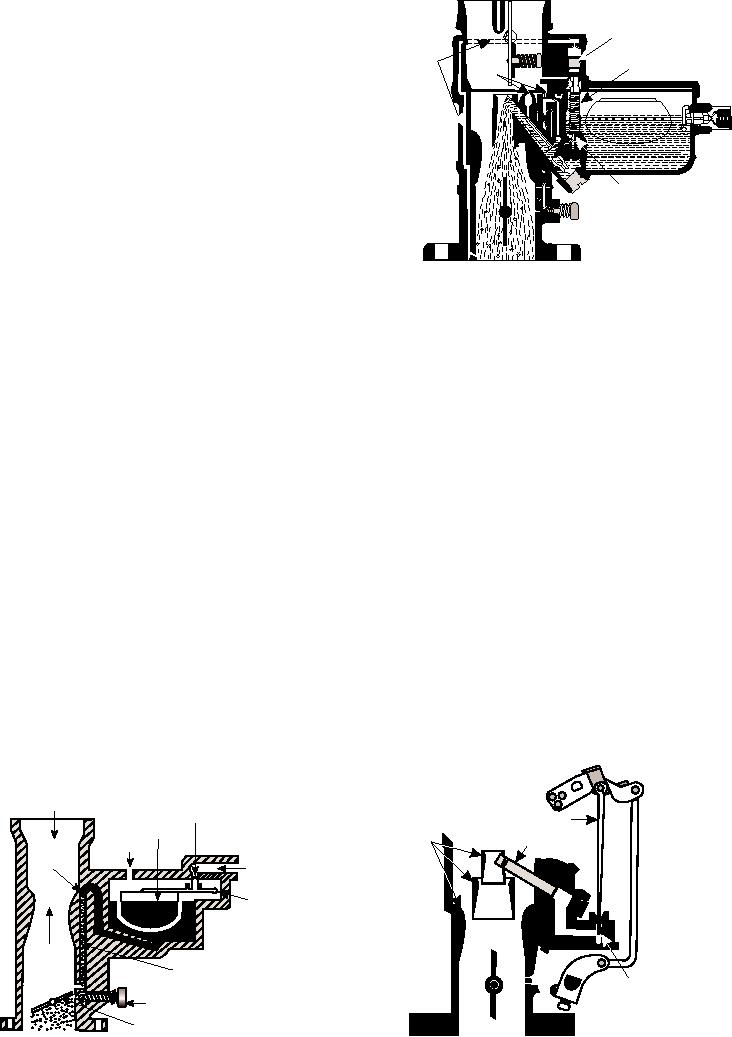
circuit (fig. 4-13). Actually, in some respects, this is
really two circuits: an idle circuit and a low-speed
VACUUM PISTON
circuit.
AIR
CHANNEL VACUUM
SPRING
BLEEDS
When the throttle is closed, there is a relatively high
vacuum in the intake manifold and below the throttle.
The idle circuit has a discharge port, or hole, that is just
below the throttle valve when it is closed. With a closed
throttle, there is a vacuum in the intake manifold and at
the discharge hole. Atmospheric pressure in the float
POWER JET VALVE
bowl will force fuel from the float bowl through the idle
circuit and out the discharge hole. An adjustable needle
valve permits more or less fuel to discharge from the
hole; this makes it possible to adjust the idling mixture
ASf04014
richness by allowing more or less fuel to discharge
during idle.
Figure 4-14.--Power jet full load circuit.
An air bleed allows air to bleed into the idle circuit
and the low-speed holes. The low-speed hole simply
when it is operating. This air mixes with the fuel and
permits more fuel to discharge into the throttle-valve
partly atomizes it before it discharges from the hole into
body as the throttle is swung away from the fully closed
the air horn. Some such assistance is needed because air
position.
movement through the horn is much slower, and there is
less tendency for atomization to take place at the hole
High-Speed Circuit
during idle. The air bleed also helps to produce fuel
flow when pressure differences (between upper and
The high-speed circuit consists essentially of the
lower portion of the air horn) are low; the mixture flows
main nozzle, which is centered in the venturi. The
more easily than liquid fuel alone.
carburetor normally contains a multiple venturi; that is,
When the throttle is opened a little, the airflow is
several venturi, one inside another. When the throttle is
still too restricted for the venturi to discharge fuel. Yet
opened sufficiently, the air passing through creates a
more air is flowing and, consequently, more fuel must
pressure difference that causes a discharge of fuel from
discharge. The idle-circuit discharge hole alone cannot
the nozzle. Throughout the intermediate- and
supply this additional fuel. To supply the additional fuel
high-speed range, this discharge increases with the
needed for this low-speed operation, an additional hole
volume of air passing through so that a fairly uniform
(low-speed discharge hole or port) is included in the
fuel-air mixture ratio is maintained. Assisting in
idle circuit. This hole is placed so that it is slightly
maintaining this fairly constant ratio is an air bleed that
above the edge of the throttle valve when it is closed,
is incorporated in the nozzle. With increased airspeed
but slightly below the edge of the throttle valve when it
through the venturi, increased air bleeding into the
is opened a small amount. In this latter position, intake
main nozzle takes place, preventing overrichness. Note
manifold vacuum can act on the low-speed hole, and
the air bleeds in figures 4-14 and 4-15.
therefore supply additional fuel from the bowl through
the circuit. The same circuit is used by both the idle-
AIR HORN
NEEDLE
VALVE
METERING ROD
FLOAT
VENTURI
AIR BLEED
VENT
AIR
BLEED
FUEL
INLET
PIVOT
VENTURI
IDLE AND LOW-
HIGH SPEED JET
SPEED CIRCUIT
IDLE MIXTURE ADJUSTMENT
THROTTLE VALVE
ASf04015
ASf04013
Figure 4-13.--A simple idle and low-speed circuit.
Figure 4-15.--Metering rod full load circuit.
4-9

