Fuel pumps are classified as positive and
During the suction stroke of a mechanical fuel
nonpositive diaphragm. The positive type continues to
pump, the rotation of an eccentric on the camshaft
pump fuel even when the carburetor bowl is filled, and
moves the pump operating arm, which pulls the
thus requires a method of bypassing the fuel back to the
diaphragm lever and the diaphragm downward. This
tank. The nonpositive diaphragm pump is the one
downward motion against the pressure of the
usually found in gasoline engines. It delivers fuel to the
diaphragm spring produces a vacuum in the pump
carburetor only when it is needed for the requirements
chamber. The vacuum holds the outlet valve closed,
of the engine.
while atmospheric pressure pushes the inlet valve open,
and fuel is delivered from the supply tank. The fuel
One type of electric fuel pump uses a motor to drive
flows through the inlet up through the filter screen, and
a set of gears, impeller, or centrifugal rotor (fig. 4-7),
down through the inlet valve into the pump chamber.
and is installed directly in the tank compartment. The
During the return stroke, the diaphragm is forced up by
inlet of the pump is submerged in the fuel. This is a
the diaphragm spring, the inlet valve closes, and the
positive displacement pump, and return lines are
outlet valve is forced open. This action allows the fuel
necessary to bring excess fuel back to the tank.
to flow through the outlet to the carburetor.
FUEL LINES
The diaphragm operating lever is hinged to the
pump arm at the arm pivot so that it can be moved down
Fuel lines connecting the various units of the fuel
but cannot be raised by the pump arm. The pump arm
system have traditionally been made of copper tubing.
spring makes that arm follow the cam without moving
However, copper tubing is being replaced by steel
the lever. The lever is moved upward only by the
tubing, which is rustproofed by copper or zinc plating.
diaphragm spring. The pump, therefore, delivers fuel to
For more information about cutting and fitting tubing,
the carburetor only when the fuel pressure in the outlet
refer to Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring
is less than the pressure maintained by the diaphragm
Tools, NAVEDTRA 14256. Three kinds of fittings are
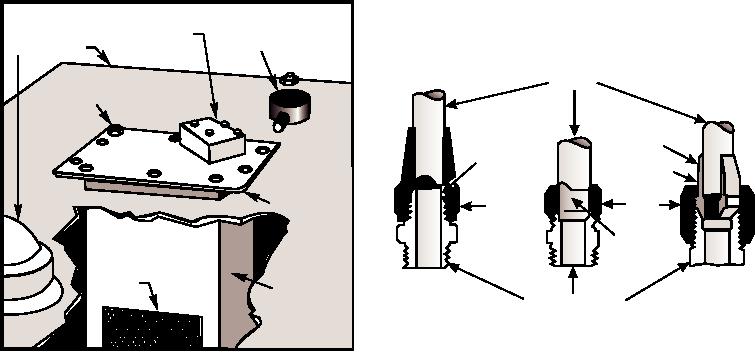
spring. This condition arises when the fuel passage
shown in figure 4-8. These are the flared, compression,
from the pump into the carburetor float chamber is open
and soldered types. Of the three, the flared fitting is
and the float needle valve is not seated. The carburetor
most common.
float and needle valve control the fuel level in the
carburetor. On some fuel pumps, a dome-shaped air
Fuel lines are placed away from exhaust pipes,
chamber is added to smooth out the pulsation (surging)
of fuel being pumped.
cause vapor locks. They are attached to the frame,
engine, and other units so that the effects of vibration
will be minimized. Fuel lines should be free of contact
ELECTRICAL
with sharp edges that might cause wear. In places of
FUEL GAUGE
FUEL
CONNECTOR
FILL
SENDING UNIT
excessive movement, as between a vehicle frame
TA N K
PIPE
TUBES
FUEL
OUTLET
SOLDERED
FLARE ON
HERE
TUBE END
SLEEVE
NUT
GASKET
NUT
BALL
SLEEVE
(FERRULE)
A
C
F I LT E R
FUEL PUMP
CONNECTORS
HOUSING
ASf04008
B
ASF04007
Figure 4-8.--Types of fittings used on fuel lines. (A) Flared.
(B) Compression. (C) Soldered.
Figure 4-7.--Tank unit type of electric pump.
4-6

