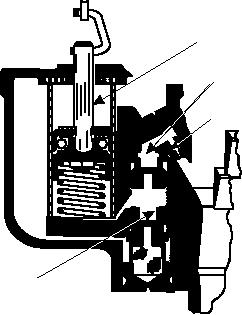
When the throttle is opened, the pump plunger
Accelerator Pump Circuit
moves downward in its cylinder. If the plunger is
The accelerator pump circuit controls a small
mechanically operated, the downward movement will
amount of fuel that is momentarily discharged into the
be brought about by direct linkage with the throttle. If it
airstream when the throttle is opened quickly. This
is vacuum-actuated, a sudden throttle opening will
extra amount of fuel is necessary to ensure
cause the manifold vacuum to drop, allowing the
instantaneous response from the engine on accelera-
accelerator pump spring to force the pump plunger
tion. When the throttle is suddenly opened, air rushes
down in the cylinder. In either case, the subsequent
through both the carburetor and the intake manifold.
action of the accelerator pump circuit is the same. The
The air is lighter than the liquid fuel and gets into
downward travel of the plunger forces fuel past the
motion quicker, so it reaches the manifold before the
discharge check valve to the accelerating jet, which
fuel charge supplied by the high-speed system. This
meters the rate at which it is discharged into the air
results in a momentarily lean mixture and hesitation
stream.
during fast acceleration. To counteract this condition,
Fuel is supplied to the pump cylinder through the
additional fuel must be supplied; this is accomplished
intake check valve at the bottom. The level of fuel in the
by the accelerator pump circuit.
pump cylinder when the plunger is held up to the top of
The accelerator pump circuit consists of the
its stroke is approximately equal to the level in the fuel
following components:
bowl. The intake check valve in the bottom of the
cylinder permits a supply of fuel to reach the cylinder,
A pump cylinder.
but the valve closes on the downstroke of the plunger,
A plunger, mechanically actuated by a
preventing the fuel in the cylinder from being pushed
back into the bowl. The accelerator pump discharge is
lever mounted on the throttle shaft, or
needed only momentarily when the throttle is opened
vacuum-operated by intake manifold vacuum.
suddenly. To prevent the accelerating jet from flowing
An intake check valve located in the bottom of
at constant throttle openings, some models have an
the pump cylinder to control the passage of fuel
air-vent check valve placed between the accelerating jet
from the bowl into the pump cylinder.
and pump cylinder above the fuel level. At steady
A discharge check valve.
part-throttle positions, when the pump plunger is
inoperative, no pressure exists on the fuel in the pump
An accelerating jet to meter the amount of fuel
cylinder. Under this condition, the air-vent check valve
used.
will be open and the air will enter the passage
connecting the pump cylinder and accelerating jet,
A typical arrangement with a mechanically
preventing fuel from flowing through the jet. The
actuated plunger is shown in fig. 4-17.
pressure on the fuel, created by the downstroke of the
pump plunger, causes the air-vent check valve to close
against its seat to prevent the fuel from being
PUMP PLUNGER
discharged back into the bowl through the air-vent
passage. On some carburetors, the area above the
DISCHARGE
plunger is connected to the intake manifold so that the
CHECK VALVE
accelerator pump does not work while the engine is not
JET
running. Under these conditions, the pressure in the
intake manifold is near atmospheric and holds the
pump plunger down.
Successful operation of the accelerator pump
depends on a delayed action, which provides a
continual stream of fuel from the pump jet after the
throttle has ceased moving. This delayed action takes
INTAKE
CHECK
care of the fuel demands of the engine in the interval
VALVE
that exists between the time the throttle is opened
ASf04017
and the time the high-speed nozzle begins to discharge
fuel.
Figure 4-17.--Carburetor accelerator pump circuit.
4-11

