nickel and carries the fuel. The outer pipe is steel and
serves as an armor casing. The outer pipe also serves
to contain a protective jacket of inert nitrogen gas at
3 psi around the inner piping. A pressure gage for the
double-walled piping is installed in the pump room to
indicate the pressure in the piping. The gage has a
range of zero to 15 psi.
If the outer casing is pierced, the nitrogen gas will
leak out. The resulting drop in pressure will be indicated
on the gage. Also, if a rupture should occur in the fuel
line inside the steel casing, the resulting increase in
pressure will be indicated on the gage. Isolate the piping
until the cause has been determined.
Expansion bellows are provided in the outer
casing to avoid strains in the casing due to unequal
expansion, which may result in leakage of the
nitrogen gas. Drain plugs in the bellows can be used
to determine whether any leaks have occurred in the
inner piping. Brass liners soldered to the outside of
the inner piping and steel spacers welded to the
inside of the outer piping are placed at intervals of
about 5 feet. These serve to hold the inner piping in
the center of the outer piping and still allow for
movement caused by expansion and contraction
between the two pipes. The outside piping is about 2
inches larger than the inner piping.
An inert gas connection, for charging the outer
piping, is provided at the lower or inboard end of the
double-walled piping. The outer piping is also
provided with a relief valve to avoid excess pressure.
The released inert gas is vented to the atmosphere
through separate piping. The relief valve is set at 15
psi.
AUTOMATIC PRESSURE-
REGULATING SYSTEM
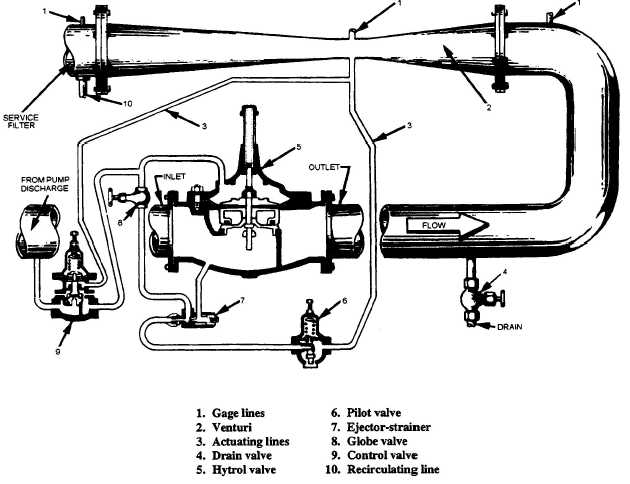
The pressure-regulating system (fig. 6-12) used in
MOGAS risers is identical for all class ships except for
size and pressure settings. This section deals with a
typical regulating system without reference to size
Figure 6-12.—MOGAS pressure-regulating system.
6-12