To standardize cargo movements and docu-
mentation, MILSTAMP interfaces with UMMIPS and
the following publications:
l Military Standard Requisitioning and Issue
Procedures (MILSTRIP)
. Military Supply and Transportation Evaluation
Procedures (MILSTEP)
l Military Standard Marking for Shipment and
Storage, MIL-STD 129 (series)
. Customs Inspections (DOD 5030.49-R)
l Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR)
MILSTAMP also specifies responsibilities of
shipping/receiving activities, clearance for routing of
material, and cargo terminal operations.
DOCUMENTATION
The movement control document for all CONUS
shipments by a commercial carrier is the government or
include shipments by QUICKTRANS. QUICKTRANS
shipments may use Transportation Control and
Movement Document (TCMD), DD Form 1384 or DD
Form 1348-1/1A as documents. Shipments originating
from an overseas point, moving within the DTS, use
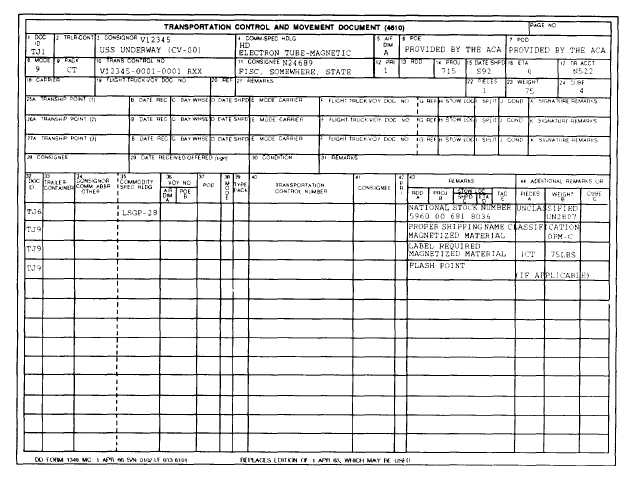
TCMD. Figure 7-16 shows an example of a TCMD. The
basic data elements required to prepare TCMD are the
same from the original MILSTRIP requisition. (See
DOD 4500.32-R, appendix D, or NAVSUP P-485,
chapter 7).
PREPARATION OF THE TCMD
Specific data elements on the TCMD provide a
summary of essential transportation data. The following
texts describes other required entries when filling out
the TCMD.
Block 1—Document Identifier. Enter TX1 for
general cargo, TJ1 for hazardous material, or TE1 for
ammunition.
Block 4—Commodity and Special Handling. This
commercial bill of lading (GBL/CBL). It does not
is a code that describes the type of cargo.
Figure 7-16.-Transportation Control and Movement Document, DD Form 1384.
7-29