Figure 1-16.--Simplified all-purpose material
symbol.
DIAGRAMS AND EQUIPMENT
Figure 1-17.--Isometric drawing of a clevis.
LAYOUTS
Drawings and equipment layouts are the universal
language used by engineers and technicians. They convey
all the necessary information to the individual who will
maintain, operate, and repair the equipment and
machinery.
To complete assigned tasks, a GSM must be able to
read and understand various types of machine
(equipment) and piping drawings and system diagrams.
To read any machine or piping drawings or system
diagrams, you must be familiar with the common terms
and standard symbols used for these drawings and
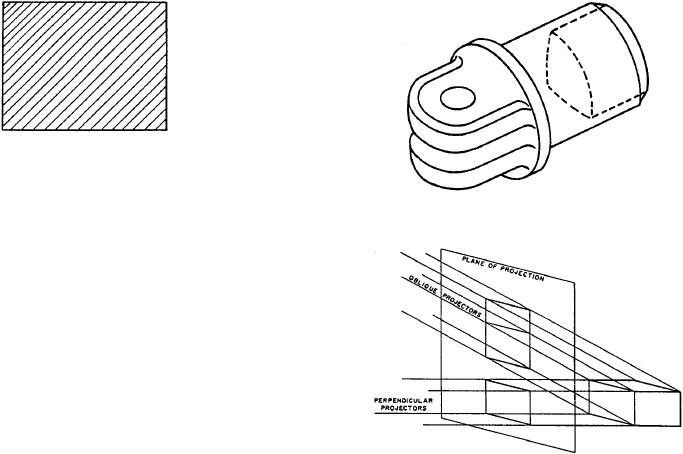
Figure 1-18.--Oblique and orthographic projections.
diagrams.
Slots and Slides
COMMON TERMS AND SYMBOLS
Slots and slides are for the mating of two specially
GSMs use drawings and diagrams in the installation,
shaped pieces of material. Though secured together, the
maintenance, and repair of shipboard equipment and
pieces can still move or slide.
systems. The following sections will provide a brief
description of these common terms and symbols. For more
Casting
detailed information, refer to Blueprint Reading and
Sketching, NAVEDTRA 10077-F1.
Casting refers to the process of making an object by
pouring molten metal into a mold (normally of sand) of the
Tolerances
desired shape and allowing it to cool.
Tolerances represent the total amount by which a
Forging
specific dimension may vary. Tolerances may be shown on
drawings by several different methods. The unilateral
Forging is a process of shaping metal while it is hot or
method is used when variations from the design size is
pliable. The hammering or forging process is done either
permissible in one direction only. In the bilateral method,
manually (blacksmith) or by machine.
a dimension figure will show the plus or minus variation
that is acceptable. In the limit dimensioning method, the
Key
maximum and minimum measurements are shown.
A key is a small wedge or rectangular piece of metal
Fillets and Rounds
inserted in a slot or groove between a shaft and a hub to
prevent slippage.
Fillets are concave metal corner (inside) surfaces. In
casting, a fillet normally increases the strength of a metal
Keyseat
corner. A rounded corner cools more evenly than a sharp
corner, thereby reducing the chance of a break. Rounds or
A keyseat is a slot or groove into which the key fits.
radii are edges or outside corners that are rounded to
prevent chipping and to avoid sharp edges.
Keyway
A keyway is the slot or groove within a cylindrical tube
or pipe into which a key fitted into a keyseat will slide.

