and stiffening requirements have resulted in an
specific aircraft should be consulted for the critical
overstrength skin with a high margin of safety. This
areas where aerodynamic smoothness must be
repair provides strength and stiffness equivalent to
maintained. An aerodynamic filler is available for
specific design requirements rather than the original
negligible damage, steps, and gaps. In many sections
structure of the material. The 100-percent stress
the skin is Chem-Milled or machined. Chem-Mill is a
intensity repair makes the strength of the repaired skin
process whereby the proper shape and size are obtained
equal to or greater than the original undamaged skin.
by a chemical acting on the metal. The proper shape
This type of skin usually has a low margin of safety.
and thickness of machined skin are obtained with the
use of a shaper or milling machine. Some skin is
Lap Patches
manufactured with lands on the metal, which is a
thicker portion of the skin where bulkheads and frames
A lap patch is an external patch that has the edges
are attached.
of the patch and the skin overlapping each other. The
One of the factors that determine the exact
overlapping portion of the patch is riveted to the skin.
procedure to be used in making skin repairs is the
On some aircraft, lap patches are permitted in certain
accessibility of the damaged area. Much of the skin on
areas, but only where aerodynamic smoothness is not
an aircraft is inaccessible from the inside. The skin in
important. In areas where it is permitted, the lap patch
such areas is referred to as "closed skin." Skin that is
may be used in repairing cracks as well as small holes.
accessible from both sides is called "open skin."
To repair cracks, you should always drill a small
Repairs to open skin may usually be made in the
hole (normally called stop drilling) in each end of the
conventional manner using specified types of standard
crack before applying the patch. Normally, you will use
rivets. To repair closed skin, some types of special blind
a No. 30 or No. 40 drill bit for this task. This prevents
fasteners must be used. The exact type of fastener used
the concentration of stresses at the apex of the crack and
will depend upon the type of repair made and the
distributes the stresses around the circumference of the
recommendations of the aircraft manufacturer.
hole. The patch must be large enough to install the
Another of the important factors to be considered
required number of rivets as determined from the rivet
when you are making a skin repair is the stress intensity
schedule indicated for the gauge material in the area
of the damaged panel. For example, certain skin areas
that is damaged. See figure 4-58. The recommended
are classified as highly critical, other areas as
patch may be cut in a circular, square, rectangular, or
semicritical, while still other areas may be classified as
diamond shape. The edges are normally chamfered
noncritical. Repairs to damages in highly critical areas
(beveled) to an angle of 45 degrees for approximately
must provide 100-percent strength replacement;
one-half its thickness.
semicritical areas require 80-percent strength
The rivet pattern is laid out on the patch by using
replacement; and noncritical areas require 60-percent
the proper edge distance and spacing. The installation
strength replacement. When a repair specifies it must
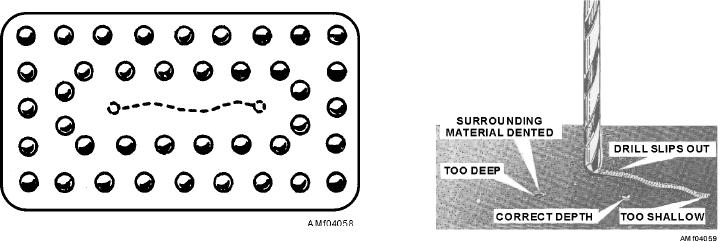
position of each rivet is marked with a center punch.
provide 60-percent strength replacement, this indicates
The impression in the material made with the center
the amount of repair strength necessary to maintain a
punch helps to keep the drill from slipping away from
margin of safety on skin areas. The 60-percent stress
the hole being drilled. See figure 4-59. Drill only a
intensity repair is specified when production methods
Figure 4-58.--Lap patch for repairing a crack in stressed skin.
Figure 4-59.--Drilling holed for rivets.
4-36

