Corrosion-Resistant Steel Tubing
Tubing assemblies are used to transport liquids or
gas (usually under pressure) between various
Corrosion-resistant steel tubing (CRES) is used in
components of the aircraft system. Tube assemblies are
high-pressure hydraulic systems (3,000 psi and above)
used in aircraft for fuel, oil, oxidizer, coolant, breathing
such as landing gear, wing flaps, and brakes. The tubing
oxygen, instruments, hydraulic, and vent lines. You
does not have to be annealed for flaring or forming. The
must be familiar with the procedures for testing and
flared section is strengthened by cold working and
fabricating tubing assemblies, and you must recognize
consequent strain hardening. Table 10-9 lists the most
the various tools and equipment and how to identify the
commonly used corrosion-resistant steel tubing in
different uses of tubing in naval aircraft. Tube
naval aircraft and includes some of the designations by
assemblies are fabricated from rigid tubing and
which the corrosion steel tubing is known. Application
associated fittings.
notes are intended as guidelines.
RIGID TUBING
Corrosion-resistant steel tube assemblies fabri-
cated with corrosion-resistant steel tubing MIL-T-6845
The tubing used in the manufacture of rigid tubing
are authorized for repair or replacement for any line
assemblies is sized by outside diameter (OD) and wall
provided no attempt is made to weld or braze the
thickness. Outside diameter sizes are in sixteenth-inch
tubing. MIL-T-6845 tubing is not to be substituted for
increments; the number of the tube indicates its size in
British DTD-5016 annealed stainless steel tubing.
sixteenths of an inch. Thus, No. 6 tubing is 6/16 or 3/8
inch; No. 8 tubing is 8/16 or 1/2 inch, etc. Wall
Aluminum Alloy Tubing
thickness is specified in thousandths of an inch.
The most common types of tubing are the
Aluminum alloy tubing is used for both
corrosion-resistant steel tubing for high pressure and
high-pressure and general-purpose lines. Table 10-10
the aluminum alloy tubing for high pressure and
lists the most commonly used aluminum alloy tubing
general-purpose.
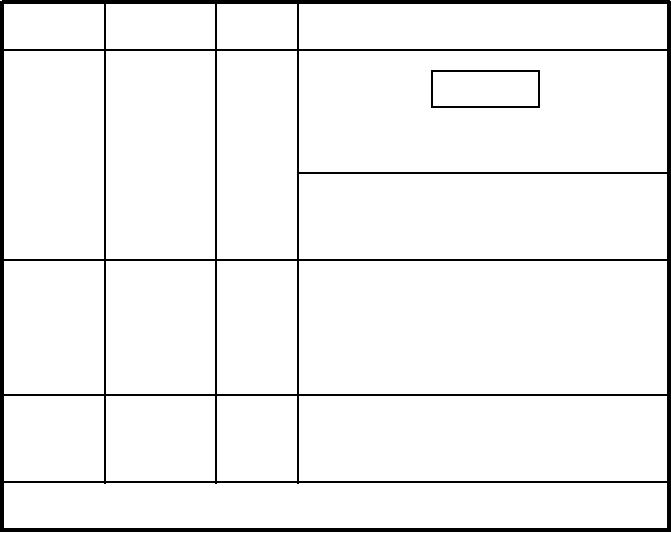
Table 10-10.--Aluminum Alloy Tubing Applications
Old
New
Type
General Usage and Applications
Specification
Specification
1100
WW-T-383
WW-T-700/1
- 0
CAUTION
-H12
-H14
Tubing conforming to Federal Specification WW-T-700/1
-H16
shall not be used in hydraulic systems.
-H18
Specification covers tempers from annealed to full-hard.
Used mostly in O-annealed condition. Good formability.
Used where high strength is not necessary, as in low- or
negative-pressure (nonhydraulic) lines.
5052
Specification covers tempers from annealed to full-hard.
WW-T-787
WW-T-700/4
- 0
Used mostly in O-annealed condition. Has good
workability. Used in medium-pressure systems (1500 psi
-H32
max.)
-H34
-H36
-H38
Specification covers annealed and three heat-treated
6061
WW-T-789
WW-T-700/6
- 0
tempers. Used mostly in O-annealed and T-6. Has good
- T4
workability. Tubing conforming to Federal Specification
1
WW-T-700/6 shall not be used in hydraulic systems.
-T6
1Only 6061-T6 is of sufficient strength to use in the repair of aluminum tubing systems. In an emergency, the
other alloys of aluminum may be used with AN fittings to make temporary repairs only.
10-25

