changes in the supply pressure (as long as the
valve to open, thereby increasing the amount of
supply pressure is at least as high as the reduced
operating air pressure going from the pilot to the
pressure desired) and regardless of the amount of
diaphragm control valve. A reverse-acting pilot
reduced pressure fluid that is used.
has a lever that reverses the pilot action. In a
Various designs of pressure-reducing valves
reverse-acting pilot, therefore, an increase in
are in use. Two of the types most commonly
controlled pressure produces a decrease in
found on gas turbine ships are the spring-loaded
operating air pressure.
reducing valve (already discussed) and the air-pilot
In the diaphragm control valve, operating air
operated diaphragm reducing valve.
from the pilot acts on the valve diaphragm. The
Air-pilot operated diaphragm control valves
superstructure, which contains the diaphragm, is
are used extensively on naval ships. The valves
direct acting in some valves and reverse acting in
and pilots are available in several designs to meet
others. If the superstructure is direct acting, the
different requirements. They may be used to
operating air pressure from the control pilot is
reduce pressure, to increase pressure, as unloading
applied to the TOP of the valve diaphragm. If
valves, or to provide continuous regulation of
the superstructure is reverse acting, the operating
pressure. Valves and pilots of very similar design
air pressure from the pilot is applied to the
can also be used for other services, such as liquid-
UNDERSIDE of the valve diaphragm.
level control and temperature control.
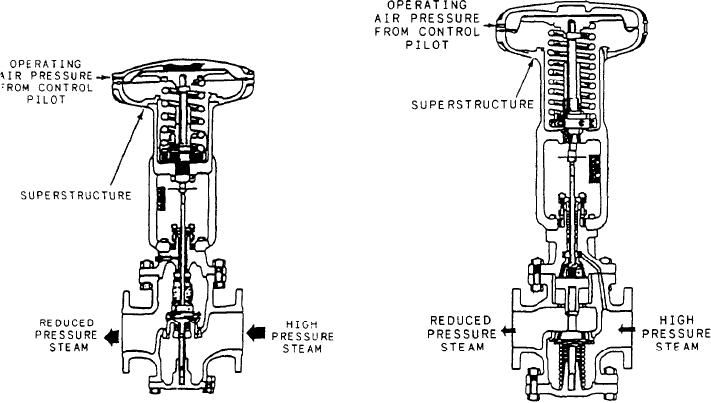
Figure 6-10 shows a very simple type of direct-
The air-operated control pilot may be either
acting diaphragm control valve with operating air
direct acting or reverse acting. A direct-acting, air-
pressure from the control pilot applied to the top
operated control pilot is shown in figure 6-9. In
of the valve diaphragm. Since the valve in the
this type of pilot, the controlled pressure-that
figure is a downward seating valve, any increase
is, the pressure from the discharge side of the
in operating air pressure pushes the valve stem
diaphragm control valve-acts on top of a
downward toward the closed position.
diaphragm in the control pilot. This pressure is
Now look at figure 6-11. This is also a direct-
balanced by the pressure exerted by the pilot
acting valve with operating air pressure from
adjusting spring. If the controlled pressure
the control pilot applied to the top of the
increases and overcomes the pressure exerted by
the pilot adjusting spring, the pilot valve stem is
forced downward. This action causes the pilot
Figure 6-10.--Diaphragm control valve, downward-seating
Figure 6-11.--Diaphragm control valve, upward-seating
type.
type.
6-7

