incorporated in the drive shaft coupling. The coupling
is driven from the engine accessory drive by a splined
may be replaced if the cause of the shearing is known
drive coupling. A shear section is provided in the
and has been remedied. Immediately after removal,
pump drive shaft to prevent damage from overload.
the pump housing should be filled two-thirds full with
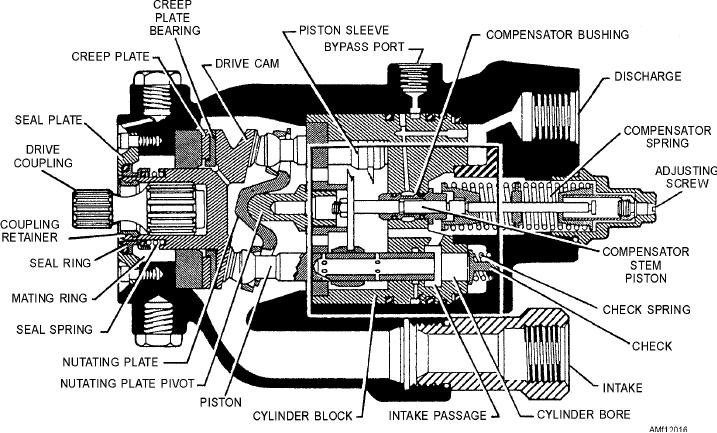
Figure 12-16 shows the internal features of the pump.
hydraulic fluid; the drive shaft couplings should be
Four major functions are performed by the internal
suitably protected by a wood block; and the ports
parts of the pump. These functions are mechanical
securely plugged to prevent the entrance of foreign
drive, fluid displacement, pressure control, and
matter.
bypass.
PISTON-TYPE PUMPS (STRATOPOWER
Mechanical Drive Mechanism.--The
VA R I A B L E D I S P L AC E M E N T ) . -- T h e r e a r e
mechanical drive mechanism is shown in figure 12-17.
s eve r a l m o d e l s o f t h e S t r a t o p ow e r va r i a b l e
Piston motion is caused by the drive cam displacing
displacement pump currently used on naval aircraft;
each piston the full height of the drive cam each
however, all are similar in principle of operation. The
revolution of the drive shaft. By coupling the ring of
pump described here is a Model 65WB06006, rated at
pistons with a nutating (wobble) plate supported by a
3,000 psi and capable of delivering 13 gallons of fluid
fixed center pivot, the pistons are held in constant
per minute at 3,800 rpm.
contact with the cam face. As the drive cam depresses
P r e s s u r e r eg u l a t i o n a n d f l ow c o n t r o l a r e
one side of the nutating plate (as pistons are advanced),
accomplished internally, automatically adjusting
the other side of the nutating plate is withdrawn an
pump delivery to meet the system demands.
equal amount, moving the pistons with it. The two
creep plates are provided to decrease wear on the
Flow cutoff begins at approximately 2,850 psi, and
revolving cam.
it reaches zero (unloads) at 3,000 psi. When the pump
is operating in the unloaded condition, the bypass
Fluid Displacement.--A schematic diagram of
system provides circulation of fluid internally for
the displacement of fluid is shown in figure 12-18.
cooling and lubrication of the pump.
Fluid is displaced by axial motion of the pistons. As
each piston advances in its respective cylinder block
The pump has three ports--the suction port, the
bore, pressure opens the check spring and a quantity of
discharge port, and the drain or bypass port. The latter
port is connected to the reservoir return line. The pump
fluid is forced past. Combined back pressure and
Figure 12-16.--Internal features of the Stratopower pump.
12-16

