tion, practice, and accurate manipulation of all layout
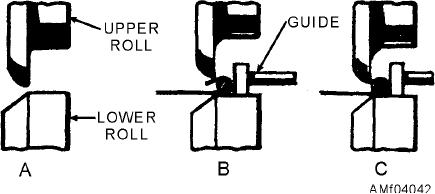
the beveled and flat surfaces meet, as shown in view A
and riveting equipment.
of figure 4-42. Adjust the guide to the position shown in
view B, then bring the top roll down so that it will turn
Rivet Selection
the edge of the metal as shown in view C. Remove the
stock from the machine by raising the top roll.
The following rules should govern your selection
CRIMPING ROLLS.--Crimping rolls are used
and use of rivets:
to make one end of a pipe smaller than the other so that
1. Replacements must not be made with rivets of
two sections may be slipped together, one end into the
lower strength material unless they are larger than those
other. A bead is placed on a pipe first, and then it is
removed. For example, a rivet of 2024 aluminum alloy
crimped. The bead forms a shoulder to keep the pipe
should not be replaced by one made of 2017 aluminum
from slipping too far into the adjoining section.
alloy unless the 2017 rivet is a size larger. Similarly,
BURRING ROLLS.--Burring is perhaps the
when 2117 rivets are used to replace 2017 rivets, the
most difficult operation to perform on a rotary machine.
next larger size should be used.
Before you place the work in the machine, make sure
2. When rivet holes become enlarged, deformed,
the cylinder or circular disc to be burred is cut or
or otherwise damaged, you should use the next larger
formed as perfectly round as possible. Then adjust the
size as replacement.
gauge on the machine so the space between the inside
of the upper roll and the gauge is set to the width of the
3. Countersunk-head rivets should be replaced by
burr. Next, place the object between the rolls and
rivets of the same type and degree of countersink, either
against the gauge. Then you should lower the upper roll
AN426 or MS20426.
until it scores the material slightly. Turn the crank
4. All protruding-head rivets should be replaced
slowly to allow the metal to slide between thumb and
with universal-head rivets, either AN470 or MS20470.
fingers. Apply a slight upward pressure as the metal
passes between the rolls. After the first revolution,
5. Rivets less than three thirty-seconds of an inch
lower the top roll and again pass the metal between the
in diameter should not be used for any structural parts,
rolls. Repeat this process, raising the edge slightly with
control parts, wing covering, or similar parts of the
each complete revolution of the material, until the edge
aircraft.
has been burred to the proper angle.
6. Minimum rivet diameter is equal to the
thickness of the thickest sheet to be riveted.
RIVETING PROCEDURES
7. Maximum rivet diameter is three times the
You must use your knowledge, ability, and
thickness of the thickest sheet to be riveted.
experience to plan an aircraft structural repair that
8. The proper length of rivet is an important part
involves riveting. Each rivet must be selected and
of the repair. If the rivet is too long, the formed head
driven in a precise manner to meet the riveting
will be too large, or the rivet may bend or be forced
specification. Some of the specifications are rivet
between the sheets being riveted. If the rivet is too
spacing and edge distance, diameter of the rivet hole,
short, the formed head will be too small or the riveted
aerodynamic smoothness, and size of the rivet bucktail.
material will be damaged. The length of the rivet should
These can be accomplished only through determina-
Figure 4-42.--Wiring operation.
4-23

