PRESSURE
Check valves are probably the most widely used
IN
RETURN
valves in fluid power systems. Check valves are also
used as integral parts of some more complex valves,
VALVE
SPOOL
such as sequence valves and counterbalance valves.
They are also used in pressure regulator valves, such as
the one pictured in figure 8-29. A variation of the check
valve--the orifice check valve--allows free flow in
one direction and a limited or restricted flow in the
opposite direction. (See figure 8-26.)
Check valves come in various designs. As shown
LEFT
RIGHT
PORT
PORT
earlier, balls, cones, and sleeves are commonly used as
A. LEFT POSITION
valve elements. Poppets, pistons, spools, and discs are
also used as valve elements in some types of check
valves.
PRESSURE
IN
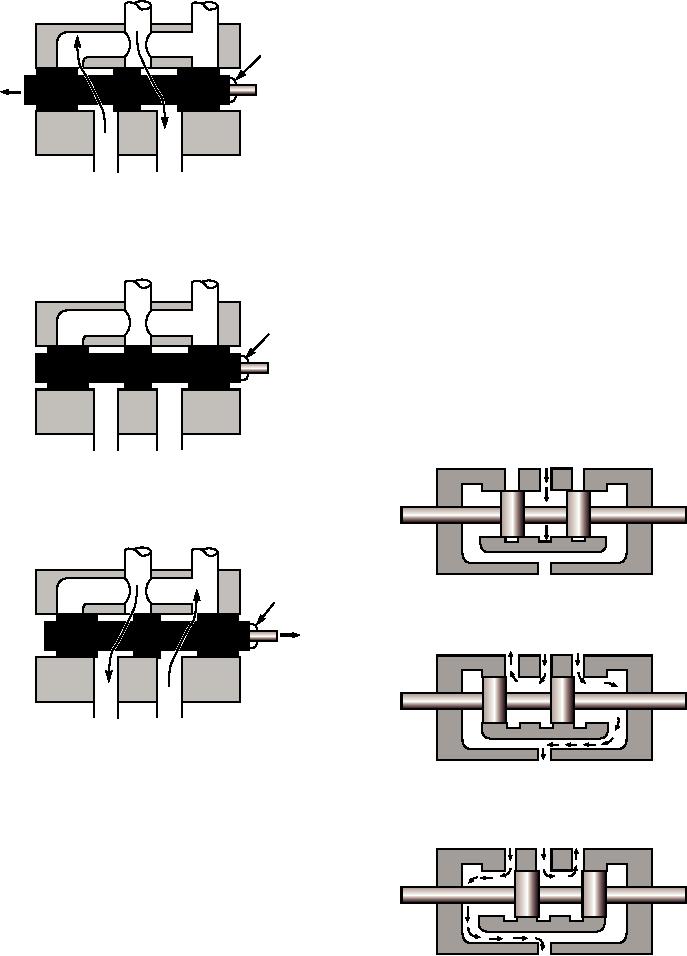
CLOSED-CENTER DIRECTIONAL CON-
RETURN
TROL VALVES.--The closed-center directional
VALVE
control valve shown in figure 8-33 is a four-way
SPOOL
control valve that is widely used in support equipment.
It has four ports--a pressure port, a return port, and two
working ports. The pressure port is connected to the
main pressure line, and the return port is connected to
the reservoir. The two working lines are connected to
C1 PRESSURE C2
LEFT
RIGHT
PORT
PORT
B. NEUTRAL
PRESSURE
IN
RETURN
RETURN
VALVE
SPOOL
A
C1 PRESSURE C2
LEFT
RIGHT
PORT
PORT
C. RIGHT POSITION
ASf08032
RETURN
Figure 8-32.--Spool directional valve.
B
CHECK VALVES.--A check valve is normally
C1 PRESSURE C2
classified as a one-way directional control valve
(although some manuals might identify them as flow
control valves). However, check valves permit flow in
one direction and prevent flow in the other. The force
of the fluid in motion opens a check valve, and it is
closed by fluid attempting to flow in the opposite
RETURN
direction, aided by the action of a spring or by gravity.
C
ASf08033
You could say that check valves are the "diodes" of the
Figure 8-33.--Closed-center directional control valve.
hydro-pneumatic world.
8-26

