RETURN
RETURN
UT TO 800 PSI
1/4 SQ.
1/4 SQ.
IN. BALL
IN. BALL
SPRING
SPRING
TENSION
TENSION
600 LBS.
600 LBS.
1 SQ. IN. PIST0N
1 SQ. IN. PISTON
MORE THAN 800 PSI
TRAPPED
UP TO 800 PSI
CHECK VALVE
CHECK VALVE
TO
TO
SYSTEM
SYSTEM
FROM PUMP
FROM PUMP
A
B
ASf08029
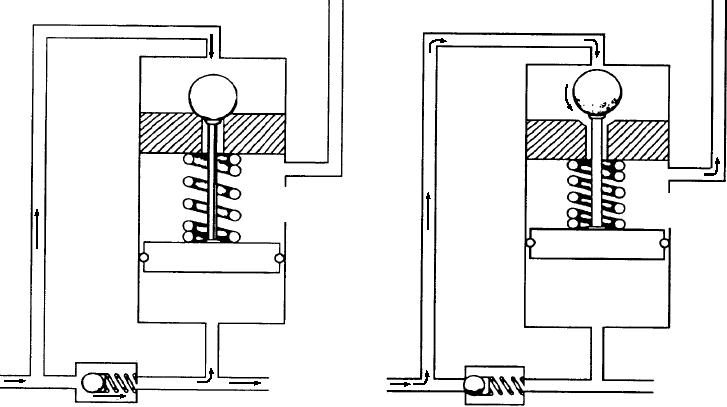
Figure 8-29.--Pressure regulator in the cut-in state (view A); and the cut-out state (view B).
element, which is the most common method. A
spring tension, the ball will remain seated. However, as
directional control valve can be one-way, two-way,
soon as that differential exceeds 600 pounds, the piston
three-way, or four-way.
will overcome the spring and lift the ball off of its seat,
as in view B of the figure.
The valve element of a directional valve may be
any one of three types:
When the ball is unseated, pressure in the top of the
valve drops immediately. At this point, the importance
A poppet--in which a piston or ball moves on
of the check valve can be seen. With the sudden
and off of a seat.
reduction in pressure, the check valve snaps shut, and
A rotary spool--in which the spool rotates about
fluid trapped in the system line continues to hold the
regulator piston in the raised position. This trapped
its axis.
fluid also maintains pressure on the system until the
A sliding spool--in which the spool slides
mechanism actuates or it is relieved by internal or
axially in a bore.
external leaking, either of which will cause the
regulator to cut back in.
Directional valves may be actuated mechanically,
manually, electrically, hydraulically, or pneumatically.
Hydraulic systems that use fixed displacement
pumps require pressure regulator valves. Those using
POPPETS.--Figure 8-30 illustrates the operation
variable displacement pumps do not.
of a simple poppet valve. The valve consists of a
movable poppet that closes against a valve seat. In the
Directional Valves
closed position, fluid pressure on the inlet side tends to
hold the valve tightly closed. Force applied to the top of
The purpose of a directional valve (also known as a
the poppet stem opens the poppet and allows fluid to
selector valve, transfer valve, or control valve) is to
flow through the valve.
control the direction of fluid flow, which, in turn,
controls the operation or direction of a mechanism.
The poppet, usually made of steel, fits into the
Such valves are classified in several ways, such as by
center bore of the seat. The seating surfaces of the
the number of ports in the valve housing, by the type of
poppet and the seat are lapped or closely machined so
control, and by the specific function of the valve.
that the center bore will be sealed when the poppet is
Another type of classification is by the type of valving
seated. An O-ring seal is usually installed on the stem
8-24

