is thrown out through the opening around the
edge of the impeller and against the side of the
casing by centrifugal force. Centrifugal force is
force that is exerted upon a body or substance by
rotation. Centrifugal force impels the body or
substance outward from the axis of rotation.
When liquid is thrown out to the edge of
the casing, a region of low pressure (below
atmospheric) is created around the center of the
impeller; more liquid moves into the eye to replace
the liquid that was thrown out. Liquid moves
into the center of the impeller with a high velocity
(speed). Therefore, liquid in the center of the
impeller has a low pressure, but it is moving at
a high velocity.
Liquid moving between the blades of the
impeller spreads out, which causes the liquid to
slow down. (Its velocity decreases.) At the same
time, as the liquid moves closer to the edge of the
casing, the pressure of the liquid increases. This
change (from low pressure and high velocity at
Figure 7-4.--Nonpositive-displacement pump.
the center to high pressure and low velocity at the
edge) is caused by the shape of the opening
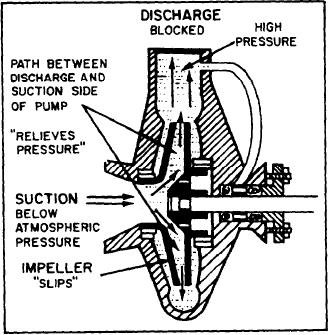
pressure cannot occur because the passages in the
between the impeller blades. This space has the
impeller (between the discharge and suction side
shape of a diffuser, a device that causes the
of the pump) act like a built-in relief valve. When
velocity-pressure relationship of any fluid that
the discharge pressure and pressure head are equal
moves through it to change.
(as in this case), the impeller is allowed to rotate
(slips) through the liquid in the casing.
A centrifugal pump is considered to be a
nonpositive-displacement pump because the
volume of liquid discharged from the pump
NOTE: Centrifugal pumps used for inter-
changes whenever the pressure head changes. The
mittent service may have to run for long periods
pressure head is the combined effect of liquid
of time against a blocked discharge. Friction
weight, fluid friction, and obstruction to flow. In
between the impeller and the liquid raises the
a centrifugal pump, the force of the discharge
temperature of the liquid in the casing and causes
pressure of the pump must be able to overcome
the pump to overheat. To prevent this, a small
the force of the pressure head; otherwise, the
line is connected between the discharge and the
pump could not deliver any liquid to a piping
suction piping of the pump.
system. The pressure head and the discharge
pressure of a centrifugal pump oppose each other.
When a centrifugal pump is started, the vent
When the pressure head increases, the discharge
line must be opened to release entrained air. The
pressure of the pump must also increase. Since
open passage through the impeller of a centrifugal
no energy can be lost, when the discharge pressure
pump also causes another problem. It is possible
of the pump increases, the velocity of flow must
for liquid to flow backwards (reverse flow)
decrease. On the other hand, when the pressure
through the pump. A reverse flow, from the
head decreases, the volume of liquid discharged
discharge back to the suction, can happen when
from the pump increases. As a general rule, a
the pressure head overcomes the discharge
centrifugal pump is usually located below the
pressure of the pump. A reverse flow can also
liquid being pumped. (NOTE: This discussion
occur when the pump is not running and another
assumes a constant impeller speed.)
pump is delivering liquid to the same piping
system. To prevent a reverse flow of liquid
Figure 7-4 shows that when the pump
through a centrifugal pump, a check valve is
discharge is blocked, nothing happens because the
usually installed in the discharge line.
impeller is hollow. A tremendous buildup in
7-4

