sampling method will be 1,870 (40,00 - 2,600 =
37,400 x 5%= 1,870). The accuracy rate is computed
mathematically by subtracting the number of errors
from the total number of items inventoried, then divide
the difference by the total number of items inventoried.
For example, the total number of items inventoried is
375 and the number of errors is 24 (375 – 24 = 351, then
351 + 375 = .9360). The accuracy rate is 93 percent.
When inventory accuracy falls below 90 percent, a
bulkhead-to-bulkhead or wall-to-wall inventory maybe
required for the storeroom or storage area involved.
All quantity and location differences found during
the random sampling inventory must be adjusted and
posted in the stock records. However, the differences
that should be counted as errors are as follows:
. Each location difference
. Each quantity difference when the quantity
adjustment exceeds 10 percent of the stock record
balance or the adjusted value exceeds .
When computing the accuracy rate, count the
location and quantity errors in the same stock record as
only one error. Changes to the cognizance symbol,
stock number, unit of issue, unit price, management
codes, and so forth that are required as a result of the
inventory are not considered as errors when computing
the inventory accuracy rate.
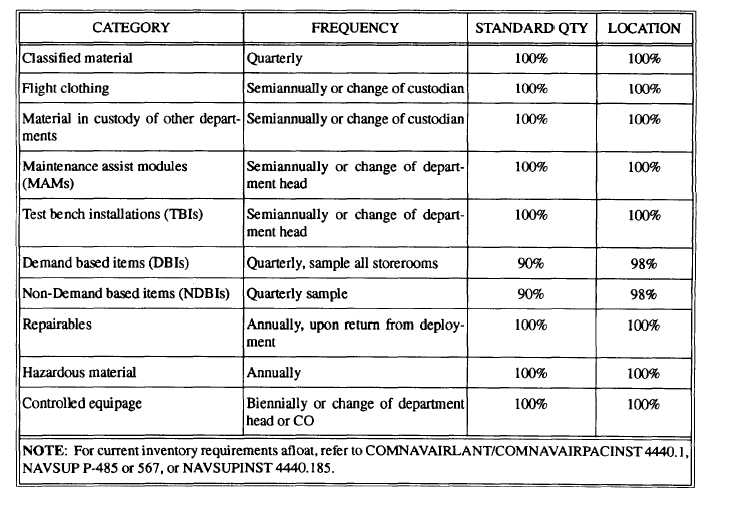
SCHEDULED INVENTORY
Some items should be inventoried at a specified
interval to ensure effective control of material needed
to support the mission. The inventory requirements in
Table 5-1 are considered the minimum necessary for
effective control of material.
NONSCHEDULED INVENTORY
This is the type of inventory that is conducted to
investigate the inaccuracies in the stock records found
during issue process, random sampling, or supply
inspection.
Nonscheduled inventories also include
those that are occasionally required of certain items as
Table 5-1.-Scheduled Inventory Requirements
5-6